Ozone Therapy: Advances in Universal Health Prevention
“`html
Ozone Therapy – An Unmatched Approach for Near Universal Prevention and Treatment
Robert Jay Rowan, MD
OPEN ACCESS
PUBLISHED 30 JUNE 2023
https://doi.org/10.1186/maxa1.4632
Abstract
Ozone therapy (OT) has been published for decades as a versatile therapy for a wide variety of conditions. The purpose of this report is to bring forward new evidence and clinical observations of its utility.
Keywords
Ozone therapy, prevention, treatment, health, medical applications
Introduction
Ozone therapy is the use of triatomic oxygen (O3), or ozone, as a therapeutic agent for the discharge of both gas and medical ozone prevention and treatment. The history of medical ozone has been covered in many published articles. Its underlying mechanism is considered to be a hormetic effect: an adaptive response of cells and organisms to a moderate (usually intermittent) stress. This aim of this article is to review the latest literature effects, and observations of the novel modality for various common medical challenges. While not going into high detail for just a few subjects, the purpose here is to present the latest findings.
Distinguished from toxic ozone (lung exposure), ozone therapy is administered in a controlled manner, and its effects are well documented. For a variety of purposes, ozone is administered via various routes including: 1. Intravenous, 2. Subcutaneous, 3. Intra-articular (as for minor joint issues), 4. Rectal, 5. Insufflation (as with ozone gas), and 6. Topical. The latter is particularly effective for skin conditions.
Mechanism of Action
OT modulates Nrf2 producing the key protective enzyme, heme oxygenase-1, a protective enzyme, along with heat shock proteins such as HSP-60, HSP-70 and HSP-90. Third, ozone modulates the kappa B nuclear factor (NF-kB) system, which regulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
OT induces cross talk between the all-important NF-kB and Nrf2 pathways1 with a net result of powerful normal immune responses and cell survival. The literature reference demonstrated OT effectively and robustly induces the Nrf2 pathway, which is favored over one-sided chemical (drug) inhibition.
Extraordinarily, ozone therapy has been shown to be effective in treating various conditions associated with accelerated cell senescence, chronic inflammation, and overall aging.2 Ozone is known to counteract biofilm resistant bacteria, and has been successfully used in treating infections.
Clinical Applications
Ozone has been particularly effective in treating viral infections. For instance, studies have shown that ozone can significantly reduce viral load in patients with Ebola virus and COVID-19 by targeting structures (such as acylated lipid residues) on their lipid/dylicoprotein coat, which prevents the virus from attaching to or entering the host cell.
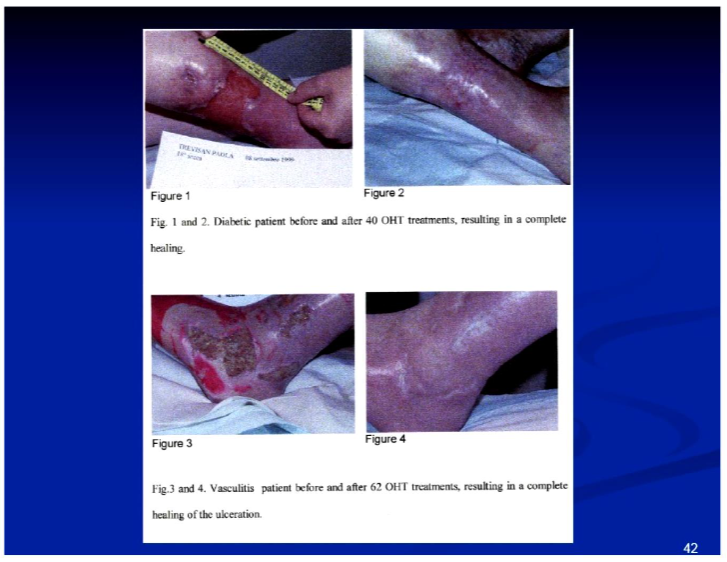
Ozone is also a non-surgical method to treat chronic pain, and has been used in various conditions including osteoarthritis, diabetes, and other inflammatory conditions. The use of ozone in dental applications has shown significant promise in treating infections and promoting healing.
Safety
Ozone has an established safety profile. Its gaseous residue is O2, a beneficial and metabolically active form. There are very few reports of problems/complications ever being published, which were of highly questionable validity. There have been reports of injury, even with the direct intravenous gas method of delivery.
Commentary
Medicine has significant apprehensions about ozone therapy, often citing concerns over potential side effects. This factor can result in a double blind controlled reporting. OT is often seen as an orphan. It is important to note that the medical community is slowly beginning to recognize the benefits of ozone therapy.
Grateful Acknowledgments for Support of OT and This Work
- Teresa Su, MD, author’s wife and practice partner
- Howard Robins, DPM, ozone therapist and leading ozone therapist
- William Zomb, DDS, retired dentist and leading ozone therapist
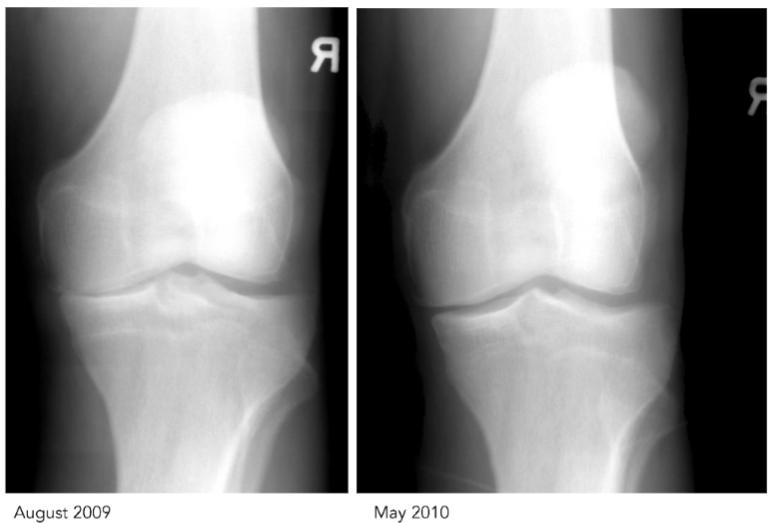
- Dennis Harper, ND, DC for graciously providing pre and post OT x-rays of treated knee.
Author’s Contributions
Robert Rowan provided 100% of the research and writing.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Financial Support
No external support provided.
References
- Bocci V. Ozone: a new medical drug. Med Hypotheses. 2006; 66: 733-42.
- Mattsson MP. Hormesis defined. Aging Res Rev. 2008 Jan;7(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2007.08.007. Epub 2007 Dec 5. PMID: 18126464; PMCID: PMC2248401.
- de Sire A, Marotta N, Ferrillo M, Agostini F, Sconza C, Lippi L, Resegotti S, Giudice A, Invernizzi M, Ammendola A. Oxygen-Ozone OT for Reducing Pro-inflammatory Cytokines: Serum Levels in Musculoskeletal and Temporomandibular Disorders. A Comprehensive Review. J Clin Med. 2023; 25(23):2582. doi: 10.3390/jcm23052582. Epub 2023 Apr 26. PMID: 35267961; PMCID: PMC9918109.
- Hashemi M, Khamehseh S.H., Dadhkan P., Mojahedi S.A. Effect of intra-articular injection of ozone in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol. Anesth. 2017; 23:27-32.
“`