Global Trends in Clinical Psychology Research 1990-2023
Global Research in Clinical Psychology Domain: A Scientometric Assessment Based on Web of Science
Pooja Sehwag1, Prof. Meera2,
OPEN ACCESS
PUBLISHED: 31 Decemeber 2024
CITATION: Pooja B. Meera, 2024. Global Research in Clinical Psychology Domain: A Scientometric Assessment Based on Web of Science. Medical Research Archives, Volume 12 Issue 12.
COPYRIGHT: © 2025 European Society of Medicine. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18103/mra.v12i12.6090
ISSN 2375-1924
Abstract
This paper attempts to examine the global research productivity and trends of clinical psychology based on Web of Science data and also highlights it from an Indian viewpoint. The study reveals a growing global interest in mental health issues. Overall, the volume of publications has increased, with the highest number produced in the form of articles. The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a drop in publications, with the relative growth rate decreasing and the doubling time increasing from 1990 to 2023. Countries like the United States, the UK, and Germany dominate the field due to their strong academic institutions and substantial funding. India collaborates most with the USA, England, and Australia. The interdisciplinary nature of clinical psychology, with overlap in neuroscience, psychiatry, and public health, has led to more comprehensive research outcomes addressing complex mental health issues. Key research areas, such as psychiatry, neuropsychology, psychopathology, family studies, health psychology, Substance abuse, and Rehabilitation, continue to drive innovation and inform evidence-based practices for advancing mental health care globally. The United States Department of Health and Human Services USA has funded the maximum number of publications globally, while the National Council on Science and Technology and the Indian Council of Medical Research have funded the most publications from India. Zvolensky Michael J has produced the maximum publications globally and Andrade Chittranjan is the topmost Indian author. The University of California System is the top affiliation globally and the National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences is the topmost affiliation from India.
1. Introduction
Clinical psychology is defined as “a branch of psychology that focuses on the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental disorders and psychological distress”. This field integrates theory, research, and clinical practice to understand and alleviate psychological problems affecting individuals across the lifespan.
Clinical psychology, as a discipline dedicated to understanding and alleviating mental health disorders through empirical research and evidence-based practice, occupies a pivotal role in modern healthcare. This discipline encompasses a broad spectrum of studies focused on psychological assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental disorders, catering to diverse populations and contexts globally. The field continually evolves, driven by the collective efforts of researchers worldwide who publish their findings in scholarly journals. A scientometric analysis offers a systematic approach to quantitatively and qualitatively assess this vast body of literature, providing insights into its growth, trends, and impact over time.
Clinical psychologists apply evidence-based interventions in various settings such as therapeutic settings, hospitals, clinics, private practices, and academic institutions. Their work aims to promote mental health and well-being through comprehensive assessment and therapeutic techniques tailored to individual needs.
The Web of Science database stands as a cornerstone in the realm of scientometrics, offering a comprehensive repository of peer-reviewed journals spanning various disciplines, including clinical psychology. Utilizing this platform allows for an in-depth exploration of the publications, citations, collaborations, and thematic developments within clinical psychology research.
This scientometric study aims to delve into the intricate landscape of clinical psychology literature as indexed in Web of Science. By employing bibliometric methods, this analysis will uncover patterns in publication output, identify key authors and institutions shaping the field, elucidate emerging research themes, and assess the impact of seminal works. Such insights not only contribute to understanding the current state of clinical psychology research but also inform future directions for scientific inquiry, policy development, and clinical practice.
Through this investigation, we aim to provide a vast perspective on how clinical psychology as a discipline has evolved within the scholarly community, highlighting its contributions to advancing knowledge, addressing societal challenges, and improving mental health outcomes globally. This analysis will serve as a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and stakeholders seeking to understand the historical context, current state, and future directions of clinical psychology research.
The literature reviewed for clinical psychology scientometrics involves examining the scholarly literature that applies scientometric methods to analyze and understand the landscape of clinical psychology research. Possibly there are no studies that have examined the scientometric aspects of the clinical psychology domain. Still, there are certain similar studies related to the psychology domain that have been reviewed so far.
Hamidi et al. examined the psychological literature on COVID-19 to shed light on the viewpoint, fields of study, and global partnerships using information from the Web of Science. The findings suggest that researchers were interested in the following areas: anxiety, mental health, delirium, loneliness, and suicide. Considering the unique circumstances that COVID-19 brought about for human cultures, psychological research is arguably one of the most significant topics in the field of health.
Wang et al. analysed research trends from 1999 to 2021 by conducting a scientometric evaluation of Positive psychology papers using the Web of Science database and found that Positive psychology is steadily expanding. The most productive countries and institutions were the United States and Harvard University, respectively.
The journal with the most co-citations was the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, while Frontiers in Psychology had the highest productivity. With 3,350 citations and 5,020 co-citations, Seligman was the author with the greatest impact. Research and development advancements in this field are centered around the COVID-19 epidemic, positive psychology intervention, character strengths, linguistic enjoyment, and systematic review.
Grover et al. used bibliometric techniques with Scopus to analyze the publication output of Indian authors on COVID-19 and psychology. Regarding citations per paper and relative citation index, authors from Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Pondicherry, had the greatest influence. The National Institute of Mental Health and Allied Sciences (NIMHANS) produced the most publications. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, with 158 papers published, was the journal with the most publications. According to the frequency with which keywords appeared, the most frequently researched themes were mental health (93), anxiety (80), and mental disease (68). They concluded that a significant amount of research on COVID-19 and psychology from India has been published.
Hulloli performed scientometric assessment of the psychology literature produced in India using the Web of Science database during 2001–2020 and revealed that the maximum literature was produced during 2019, with a slight decrement during the year 2020. Most of the papers were published in Psychiatry, and Grover S was the most productive author. He also used Web of Science to compare the quality of psychology research output between 2001 and 2020 in two different countries: South Africa and India. In terms of publishing growth, document type, language, and Activity Index, both countries were compared and it was found that 12,543 papers published in India have received 96,871 citations. South Africa, on the other hand, has published the most papers (9,938 total citations; 1,21,385).
Liu and Oakland carried out research to determine the expansion and evolution of academic writing that explicitly makes mention to the word ‘school psychology’ in the Science Citation Index between 1907 and 2014 using the Web of Science database and found that even though the database contained publications from all around the world, the majority of the articles were written by Americans. Journal of School Psychology was the most productive journal and the University of Minnesota–Twin Cities was the topmost producer.
Naveed et al. employed the Web of Science to demarcate the overall patterns of publication as well as seminal theories and areas of focus in the field of child and adolescent psychiatry. Their findings indicated a growing trend of research in this area. Research on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, PTSD, social phobia, checklists, psychopharmacology, and the design of psychometric instruments were the main areas of focus for psychiatric research, and in the field of child and adolescent psychiatry, there has been a notable surge in both innovation and development of study fields between 1980 and 2016.
2. Methodology
The present study examines the clinical psychology literature produced from 1989 to 2023 with the data extracted from the Web of Science database. The Web of Science Category ‘Clinical psychology’ was selected for analysis and the publications were refined selecting the timeframe 1989–2023.
Various bibliometric components were considered while extracting the data like year-wise data, publication type, authors, publication source, top-cited papers, institutions, funding agencies, countries, etc. The data has been downloaded, organized, tabulated, and analyzed using Ms-Excel software which is then shown in tables and graphs for interpretation.
3. Objectives
The following are the objectives for carrying out the scientometric study of global clinical psychology literature using Web of Science
-
To analyze the publication trend of clinical psychology literature and identify the growth rate and doubling period of publications over a specific time.
-
To identify the type of clinical psychology publications, prolific authors, institutions, journals, top countries producing the maximum literature in clinical psychology.
-
To assess the citation impact of clinical psychology publications by identifying highly cited papers and influential authors contributing to the field.
-
To identify the core research areas, and emerging trends in clinical psychology research through keyword analysis.
-
To identify the maximum fund-providing agencies for clinical psychology researchers.
4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
As reflected in the Web of Science database, during 35 years, i.e., 1989–2023, 276,800 publications have been produced in clinical psychology globally with 1018 publications from India.
Table 1: Chronological Distribution of the Global Publications in Clinical Psychology
| Publication Year | Publication Count | % | Cumulative | RGR (Relative Growth Rate) | Doubling time (Dt) | Mean Relative Growth Rate | Mean Doubling Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 3713 | 1.341 | 3713 | ||||
| 1990 | 4319 | 1.56 | 8032 | 0.772 | 0.082 | ||
| 1991 | 4316 | 1.559 | 12348 | 0.430 | 0.146 | ||
| 1992 | 3956 | 1.429 | 16304 | 0.278 | 0.227 | ||
| 1993 | 4486 | 1.621 | 20790 | 0.243 | 0.259 | 0.345 | 0.143 |
| 1994 | 4529 | 1.636 | 25319 | 0.197 | 0.320 | ||
| 1995 | 5225 | 1.888 | 30544 | 0.188 | 0.336 | ||
| 1996 | 5334 | 1.927 | 35878 | 0.161 | 0.391 | ||
| 1997 | 5429 | 1.961 | 41307 | 0.141 | 0.447 | ||
| 1998 | 5450 | 1.969 | 46757 | 0.124 | 0.508 | 0.162 | 0.400 |
| 1999 | 6333 | 2.288 | 53090 | 0.127 | 0.496 | ||
| 2000 | 5826 | 2.105 | 58916 | 0.104 | 0.605 | ||
| 2001 | 5999 | 2.167 | 64915 | 0.097 | 0.650 | ||
| 2002 | 5648 | 2.04 | 70563 | 0.083 | 0.755 | ||
| 2003 | 6805 | 2.458 | 77368 | 0.092 | 0.684 | 0.101 | 0.638 |
| 2004 | 6062 | 2.19 | 83430 | 0.075 | 0.835 | ||
| 2005 | 7209 | 2.604 | 90639 | 0.083 | 0.760 | ||
| 2006 | 6493 | 2.346 | 97132 | 0.069 | 0.911 | ||
| 2007 | 7632 | 2.757 | 104764 | 0.076 | 0.833 | ||
| 2008 | 7703 | 2.783 | 112467 | 0.071 | 0.888 | 0.075 | 0.845 |
| 2009 | 7863 | 2.841 | 120330 | 0.068 | 0.932 | ||
| 2010 | 9002 | 3.252 | 129332 | 0.072 | 0.873 | ||
| 2011 | 9591 | 3.465 | 138923 | 0.072 | 0.881 | ||
| 2012 | 9527 | 3.442 | 148450 | 0.066 | 0.950 | ||
| 2013 | 10148 | 3.666 | 158598 | 0.066 | 0.953 | 0.069 | 0.918 |
| 2014 | 10110 | 3.652 | 168708 | 0.062 | 1.019 | ||
| 2015 | 10121 | 3.656 | 178829 | 0.058 | 1.081 | ||
| 2016 | 10745 | 3.882 | 189574 | 0.058 | 1.080 | ||
| 2017 | 10187 | 3.68 | 199761 | 0.052 | 1.204 | ||
| 2018 | 10314 | 3.726 | 210075 | 0.050 | 1.251 | 0.056 | 1.127 |
| 2019 | 14141 | 5.109 | 224216 | 0.065 | 0.967 |
| Publication Year | Publication Count | % | Cumulative | RGR (Relative Growth Rate) | Doubling time (Dt) | Mean Relative Growth Rate | Mean Doubling Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 13049 | 4.714 | 237265 | 0.057 | 1.114 | ||
| 2021 | 14737 | 5.324 | 252002 | 0.060 | 1.045 | ||
| 2022 | 12702 | 4.589 | 264704 | 0.049 | 1.281 | ||
| 2023 | 12096 | 4.37 | 276800 | 0.045 | 1.410 | 0.055 | 1.163 |
| Total | 276800 |
Table 1 and Figure 1 present the chronological distribution of clinical psychology publications produced globally from 1989 to 2023. It can be depicted that the maximum number of publications have been produced during the year 2021 i.e., 14,737 (5.324%), followed by 2019 (14,141; 5.109%), and 2020 (13,049; 4.714%).
The lowest number of publications was produced in 1989, i.e., 3,713 (1.341%). Though fluctuations in the data have been observed throughout the time frame, the noticeable number of publications dropped after the year 2019. This could be attributed to several potential factors such as many research activities being disrupted due to lockdowns, which affected data collection, participant recruitment, and overall research progress.
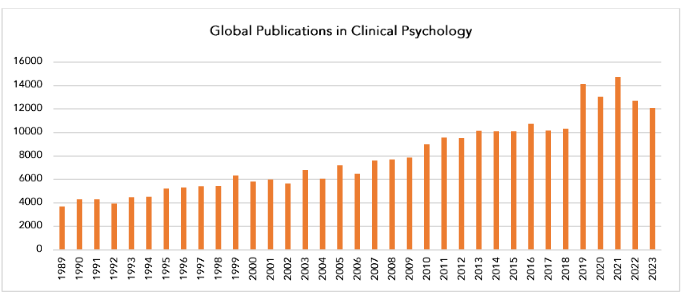
Figure 1: Chronological Distribution of the Global publications in Clinical Psychology
Funding and research priorities shifted to address the pandemic, which may have diverted attention and resources away from clinical psychology research. The peer review and publication process itself may have experienced delays due to the increased volume of submissions related to COVID-19 and the adjustments made by journals and publishers to handle the crisis.
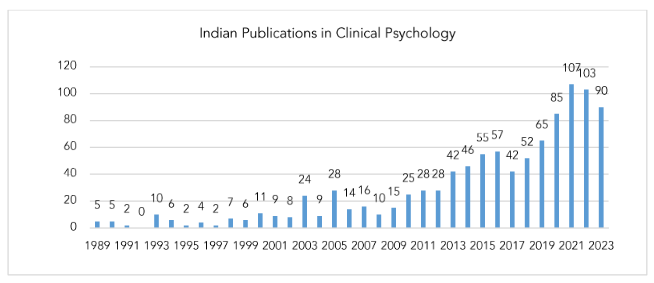
Figure 1: Chronological Distribution of the Global Publications in Clinical Psychology
The chronological distribution of the Indian publications is visible in figure 1.1. The maximum number of papers produced was in the year 2021 (107 papers), followed by 2022 (103) and 2023 (90), with the least number of publications in 1991 (2 publications). No publications have been produced during 1992 from India in the field of clinical psychology, the reason being that Web of Science may not have comprehensive coverage of all journals, especially older ones. Some journals from 1992 might not be included in their database or might not have been indexed at that time.
Table 1 and Figure 1.3 represent the relative growth rate and doubling time of the global publications in clinical psychology. It can be depicted that the Relative Growth Rate of publications has decreased from 0.772 in 1990 to 0.045 in 2023.
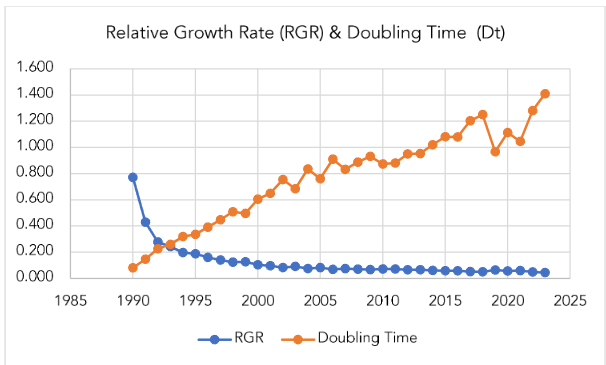
Figure 1.3: Relative Growth Rate and Doubling time of publications
On the other hand, the Doubling time for the publications has increased from 0.082 in 1990 to 1.410 in 2023. Both the RGR and Doubling time show fluctuations in between. The mean RGR is least during the time frame 2019–2023 i.e., 0.056, and maximum during 1989–1992 i.e., 0.345.
The mean doubling time for the publications is maximum during the years 2019 to 2023, i.e., 1.163, while it is minimum during the years 1989 to 1992, i.e., 0.143. This also depicts that the RGR is inversely proportional to the doubling time.
Table 2: Type of Publications
| Sr. no. | Type of Publications | Publication count | % of Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Article | 194,310 | 70.199 |
| 2 | Meeting Abstract | 33,218 | 12.001 |
| 3 | Book Review | 16,062 | 5.803 |
| 4 | Review Article | 12,309 | 4.447 |
| 5 | Editorial Material | 12,165 | 4.395 |
| 6 | Proceeding Paper | 6,694 | 2.418 |
| 7 | Letter | 4,036 | 1.458 |
| 8 | Note | 1,206 | 0.436 |
| 9 | Biographical-Item | 545 | 0.197 |
| 10 | Book Chapters | 407 | 0.147 |
| Sr. no. | Type of Publications | Publication count | % of Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | News Item | 221 | 0.080 |
| 12 | Item About an Individual | 109 | 0.039 |
| 13 | Bibliography | 88 | 0.032 |
| 14 | Software Review | 43 | 0.016 |
| 15 | Retracted Publication | 40 | 0.014 |
| Others (13) |
Table 2 and figure 2 represent the type of publications produced in the clinical psychology domain. A total of 28 document types have been recorded including articles, book reviews, abstracts, review papers, editorials, proceeding papers, letters, notes, biographical items, book chapters, news items, retracted publications, and many more.
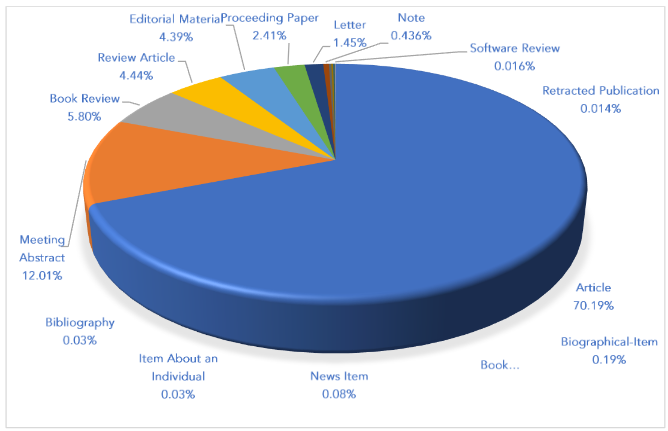
Figure 2: Type of publications
The maximum number of publications has been produced in the form of articles, i.e., 194,310 (70.199%), followed by meeting abstracts i.e., 33,218 (12.001%), and book reviews (16,062; 5.803%).
Table 3: Top Authors of Clinical Psychology
| Rank | Top Authors | Affiliation | Country | Publications | % | h-index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zvolensky Michael J | University of Houston | USA | 465 | 0.168 | 71 |
| 2 | Strauss Bernhard | Voestalpine AG | Austria | 443 | 0.160 | 38 |
| 3 | Petermann Franz | University of Bremen | Germany | 398 | 0.144 | 53 |
| 4 | Brahler Elmar | University of Leipzig | Germany | 374 | 0.135 | 82 |
| 5 | Treasure J | King’s College London | England | 344 | 0.124 | 99 |
| 6 | Joiner TE | Florida State University | USA | 342 | 0.124 | 97 |
| 7 | Rief Winfried | Philipps University Marburg | Germany | 330 | 0.119 | 80 |
| 8 | Schmidt Norman B | Florida State University | USA | 317 | 0.115 | 69 |
| 9 | Bulik Cynthia M | University of North Carolina | USA | 316 | 0.114 | 78 |
| 10 | Crosby Ross D | Sanford University | USA | 287 | 0.104 | 90 |
The top ten writers globally who have contributed the most papers in clinical psychology are shown in Table 3. Zvolensky Michael J from the University of Houston, USA has produced the maximum number of publications i.e., 465 (0.168%, Rank 1) having an h-index value equivalent to 71, followed by Strauss Bernhard from Voestalpine AG, Austria (443 publications, 0.16%, Rank 2) having h-index = 38, and Petermann Franz from University of Bremen, Germany having 398 publications (0.144%, Rank 3) having an h-index equal to 53.
Brahler Elmar from the University of Leipzig, Germany, possesses Rank 4 contributing (374 publications, 0.135%) and has an h-index value of 83. He is found to be the highly cited award recipient from the year 2019–2023 in the subject categories Psychology, Psychiatry, Public, Environmental & Occupational Health and Oncology with 34,860 total citations.
Rief Winfried from Philipps University Marburg, Germany (Rank 7, 330, 0.199% publications) also got a highly cited researcher award from the year 2021–2023 in subject categories Psychology, Psychiatry, Neurosciences & Neurology, and Pharmacology & Pharmacy with 30,197 total citations and an h-index equal to 80.
Table 3.1: Top Indian Authors
| Indian Rank | Global Rank | Author Name | Affiliation | Papers | % | h-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 72 | Andrade Chittranjan | National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences | 159 | 15.61 | 35 |
| 2 | 6381 | Ghosh, Abhishek | Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh | 21 | 2.06 | 16 |
| 3 | 11111 | Basu, Debasish | Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh | 14 | 1.37 | 20 |
| 4 | 11306 | Dhikav, Vikas | ICMR – National Institute for Implementation Research on Non-Communicable Diseases (NIIRNCD) | 14 | 1.37 | 13 |
| 5 | 12025 | Sarkar, Siddharth | All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) New Delhi | 14 | 1.37 | 21 |
| 6 | 14402 | Kumar, Devvarta | National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences – India | 12 | 1.17 | 9 |
| 7 | 14537 | Mattoo, Surendra K | Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh | 12 | 1.17 | 22 |
| 8 | 14853 | Sagar, Rajesh | All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) New Delhi | 12 | 1.17 | 67 |
| 9 | 18728 | Janardhan Reddy, Y. C. | National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences – India | 10 | 0.98 | 42 |
| 10 | 19063 | Telles, Shirley | National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences – India | 10 | 0.98 | 29 |
Table 3.1 lists the leading Indian authors who have made the maximum contributions to clinical psychology, along with their rankings both domestically and globally. Rank 1 is possessed by Andrade Chittranjan (Global rank 72, h-index 35), affiliated with the National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences, contributing 159 papers, i.e., 15.61% of the Indian publications, followed by Ghosh, Abhishek with rank 2 (Global rank 6381, h-index 16), and Basu, Debasish with rank 3 (Global rank 11111, h-index 20) from Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research.
(PGIMER), Chandigarh, contributing 21 i.e., 2.06% and 14 i.e., 1.37% publications respectively. Among the top 10 Indian authors, 4 authors are affiliated to National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences, 3 are affiliated to PGIMER, Chandigarh, 2 are affiliated to AIIMS, New Delhi and 1 is affiliated to ICMR – National Institute for Implementation Research on Non-Communicable Diseases (NIIRNCD).
Table 4: Top International Affiliations of Clinical Psychology
| Rank | Affiliations | Country | Publications | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of California System | USA | 11362 | 4.188 |
| 2 | University of London | England | 8777 | 3.235 |
| 3 | US Department of Veterans Affairs | USA | 8092 | 2.983 |
| 4 | Harvard University | USA | 7970 | 2.938 |
| 5 | Veterans Health Administration VHA | USA | 7928 | 2.922 |
| 6 | Pennsylvania Commonwealth System of Higher Education | USA | 6685 | 2.464 |
| 7 | State University System of Florida | USA | 6600 | 2.433 |
| 8 | University System of Ohio | USA | 6562 | 2.419 |
| 9 | King’s College London | England | 5102 | 1.881 |
| 10 | University of Texas System | USA | 4925 | 1.815 |
Table 4 depicts the top most productive international affiliations of clinical psychology. Rank 1 is occupied by the University of California System, USA, contributing 11,362 (4.18%) publications. Rank 2 is held by the University of London, England, with 8,777 (3.23%) papers and Rank 3 by US Department of Veterans Affairs, USA with 8,092 (2.98%) publications. Rank 4 is occupied by Harvard University, USA with 7,970 (2.93%) publications and Rank 5 by Veterans Health Administration, USA with 7,928 (2.92%) publications.
Among the top 10 most productive affiliations in the world, 8 belong to the USA and the remaining 2 to England. US institutions dominate clinical psychology research due to significant funding, high-quality education, state-of-the-art research facilities, interdisciplinary collaboration, access to prestigious journals and conferences, diverse research opportunities, strong professional networks, and historical leadership.
Table 4.1: Top Indian Affiliations
| Indian Rank | World Rank | Name of the Affiliation | State | Publications | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 507 | National Institute of Mental Health Neurosciences | Karnataka | 249 | 24.45 |
| 2 | 1193 | All India Institute of Medical Sciences | Delhi | 63 | 6.18 |
| 3 | 1751 | Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education Research | Chandigarh | 35 | 3.43 |
| 4 | 1920 | Indian Institute of Technology System | West Bengal | 31 | 3.04 |
| 5 | 2256 | University of Delhi | Delhi | 24 | 2.35 |
| 6 | 2296 | Manipal Academy of Higher Education | Karnataka | 23 | 2.25 |
| 7 | 2514 | National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre | Uttar Pradesh | 20 | 1.96 |
| 8 | 2602 | Tata Institute of Social Sciences | Maharashtra | 19 | 1.86 |
| 9 | 2636 | Christian Medical College Hospital | Tamil Nadu | 18 | 1.76 |
| 10 | 3087 | Banaras Hindu University | Uttar Pradesh | 14 | 1.37 |
Table 4.1 lists the top affiliations of India contributing maximum research in the clinical psychology domain. It can be clearly depicted that the researchers from the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Karnataka contribute the maximum papers i.e., 249 publications (0.24.45% of the Indian publications), world rank 507. This indicates that it is a leading center for mental health research, education, and clinical services in India. Its significant contribution to clinical psychology research is attributed to its specialized focus on mental health and neuroscience, comprehensive facilities, interdisciplinary approach, high volume of clinical cases, government support, advanced training programs, collaborations with national and international research organizations, universities, and healthcare institutions, and a focus on relevant issues in the Indian context.
Rank 2 is occupied by All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi with 63 publications i.e., 6.18%, and Rank 3 is occupied by Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education Research, Chandigarh, with 35 publications i.e., 3.43%.
Table 5: Top Journals of Clinical Psychology
| Rank | Journal Titles | Publisher | Publications | % | (JCI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology | Oxford University Press, United Kingdom | 11059 | 3.995 | 0.83 |
| 2 | Journal of Clinical Psychiatry | Physicians Postgraduate Press, United Kingdom | 10832 | 3.913 | 1.15 |
| 3 | Psychological Medicine | Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom | 8557 | 3.091 | 2.36 |
| 4 | International Psychogeriatrics | Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom | 7503 | 2.711 | 1.38 |
| 5 | Addictive Behaviors | Pergamon-Elsevier Science Ltd, Netherlands | 6887 | 2.488 | 1.34 |
| 6 | International Journal of Behavioral Medicine | Springer, USA | 6515 | 2.354 | 0.71 |
| 7 | Clinical Neuropsychologist | Taylor & Francis Inc, United Kingdom | 5887 | 2.127 | 1.11 |
| 8 | Behaviour Research and Therapy | Pergamon-Elsevier Science Ltd, Netherlands | 4981 | 1.799 | 1.50 |
| 9 | Archives of Sexual Behavior | Springer, USA | 4869 | 1.759 | 1.31 |
| 10 | Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology | Taylor & Francis Inc, United Kingdom | 4822 | 1.742 | 0.61 |
* JCI = Journal Citation Indicator, recorded from Web of Science.
Table 5 enlists the top journals in which most research has been published related to clinical psychology topics.
-
Rank 1 is occupied by Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology (JCI = 0.83), published by Oxford University Press, United Kingdom with 11,059 publications (3.99%).
-
Rank 2 is occupied by Journal of Clinical Psychiatry (JCI = 1.15), published by Physicians Postgraduate Press, United Kingdom with 10,832 publications (3.91%).
-
Rank 3 is occupied by Psychological Medicine (JCI = 2.36), published by Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom with 8,557 publications (3.09%).
Among the top 10 journals, 6 are published in the United Kingdom, 2 in the USA, and 2 in the Netherlands.
Table 6: Top Countries Contributing Maximum Research in Clinical Psychology
| Rank | Countries/Regions | Publications | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 137585 | 49.705 |
| 2 | England | 25739 | 9.299 |
| 3 | Germany | 20097 | 7.260 |
| 4 | Canada | 17900 | 6.467 |
| 5 | Australia | 15039 | 5.433 |
| 6 | Netherlands | 10377 | 3.749 |
| 7 | Spain | 5950 | 2.150 |
| 8 | Peoples R China | 5009 | 1.810 |
| 9 | Italy | 4880 | 1.763 |
| 10 | Israel | 3932 | 1.421 |
| India | 1018 | 0.368 |
Table 6 enlists the top nations contributing maximum publications in the clinical psychology domain. The USA holds rank 1 contributing 137,585 papers (49.70% of the total). Rank 2 is occupied by England contributing 25,739 (9.29%), and rank 3 by Germany with 20,097 papers (7.26%). These nations are followed by Canada and Australia with 17,900 (6.46%) and 15,039 (5.43%) publications respectively.
Due to their robust academic institutions, significant financing, historical roots, multidisciplinary collaboration, worldwide influence, and strong public backing, the United States, England, and Germany are the top three nations in the world for clinical psychology research. Prominent research and academic institutions in these nations, like the University of Oxford, Stanford, and Harvard, offer strong academic settings for training and research.
A significant amount of funding is provided for psychological research by organizations like the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) in Germany, the Medical Research Council (MRC) in the United Kingdom, and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States. In these nations, interdisciplinary cooperation enables clinical psychology to interact with other disciplines, such as neuroscience, medicine, and social sciences, producing more thorough and significant research results. Strong professional networks are offered by associations such as the American Psychological Association (APA), the British Psychological Society (BPS), and the German Psychological Society (DGPs), which encourage research, establish ethical guidelines, and assist in the communication of results.
Table 6.1: Top Collaborating Countries with India
| Rank | Country | Collaborated Publications | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 203 | 19.941 |
| 2 | England | 125 | 12.279 |
| 3 | Australia | 59 | 5.796 |
| 4 | Canada | 49 | 4.813 |
| 5 | Netherlands | 40 | 3.929 |
| 6 | Peoples R China | 39 | 3.831 |
| 7 | Italy | 36 | 3.536 |
| 8 | Brazil | 35 | 3.438 |
| 9 | Switzerland | 34 | 3.34 |
| 10 | Germany | 31 | 3.045 |
Table 6.1 depicts the top collaborating countries with India for contributing publications of clinical psychology. Maximum collaborated publications with India are from the USA, i.e., 203 publications (19.94%), followed by England with 125 publications (12.27%), and Australia with 59 (5.79%) publications. By partnering with organizations in these nations, Indian researchers gain access to state-of-the-art techniques, resources, and knowledge that improve the caliber and significance of their work. The fact that English is widely spoken among scholars in these nations makes communication and cooperation easier. Mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, and trauma are typically of interest to researchers from these nations, and through cooperative endeavors, they address these problems from several angles and provide appropriate interventions.
Table 7: Most Cited Papers of Clinical Psychology
| Rank | Publication Title | Authors | Journal | Citations | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI): The development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10 | Sheehan, DV et al. | Journal of Clinical Psychiatry | 18366 | 1998 |
| 2 | The structure of negative emotional states – comparison of the depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck depression and anxiety inventories | Lovibond, PF; Lovibond, SH | Behaviour Research and Therapy | 8053 | 1995 |
| 3 | Clinical-significance – a statistical approach to defining meaningful change in psychotherapy-research | Jacobson, NS; Truax, P | Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology | 7535 | 1991 |
| 4 | Short screening scales to monitor population prevalences and trends in non-specific psychological distress | Kessler, RC et al. | Psychological Medicine | 6741 | 2002 |
| 5 | Measuring emotion – the self-assessment mannequin and the semantic differential | Bradley, MM; Lang, PJ | Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry | 5814 | 1994 |
| 6 | Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale | Patton, JH; Stanford, MS; Barratt, ES | Journal of Clinical Psychology | 5749 | 1995 |
| 7 | Development of a new resilience scale: The Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC) | Connor, KM; Davidson, JRT | Depression and Anxiety | 5655 | 2003 |
| 8 | The Pain Catastrophizing Scale: Development and validation | Sullivan, MJL; Bishop, SR; Pivik, J | Psychological Assessment | 5575 | 1995 |
| 9 | Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale | Gratz, KL; Roemer, L | Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment | 5072 | 2004 |
| 10 | Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment | Harper, A; Power, M | Psychological Medicine | 4876 |
Table 7 presents the top most cited papers during the period of study in the clinical psychology domain. The most cited paper is entitled as “The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI)” (1998) by Sheehan, DV et al. and is published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry with 18,366 citations. This indicates that it has provided significant information or a well-accepted approach, as evidenced by the fact that researchers often cite the publication in their own research. It is followed by “The structure of negative emotional states” (1995) by Lovibond, PF and Lovibond, SH published in Behaviour Research and Therapy with 8,053 citations and “Clinical-significance – a statistical approach” (1991) by Jacobson, NS and Truax, P published in Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology with 7,535 citations.
Papers with groundbreaking findings, novel methodologies, or significant advancements are often used as foundational references for subsequent research. The paper’s broad applicability, collaboration, and high-quality research enhance its credibility and attract more citations. Additionally, papers with cross-cultural or global relevance are more likely to be cited by a diverse range of researchers worldwide.
Table 8: Top Research Areas of Clinical Psychology
| Sr. no. | Subject categories | Publications | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Psychology | 276800 | 100.000 |
| 2 | Psychiatry | 92189 | 33.305 |
| 3 | Neurosciences Neurology | 24283 | 8.773 |
| 4 | Substance Abuse | 17479 | 6.315 |
| 5 | Family Studies | 16899 | 6.105 |
| 6 | Social Sciences Other Topics | 14365 | 5.190 |
| 7 | Geriatrics Gerontology | 7503 | 2.711 |
| 8 | Nutrition Dietetics | 5714 | 2.064 |
| 9 | Criminology Penology | 4324 | 1.562 |
| 10 | Pharmacology Pharmacy | 4052 | 1.464 |
| 11 | Rehabilitation | 3732 | 1.348 |
| 12 | Public Environmental Occupational Health | 2763 | 0.998 |
| 13 | Obstetrics Gynecology | 1969 | 0.711 |
| 14 | Health Care Sciences Services | 1694 | 0.612 |
| 15 | Education Educational Research | 1295 | 0.468 |
| 16 | Pediatrics | 1135 | 0.410 |
| 17 | Biomedical Social Sciences | 724 | 0.262 |
| 18 | Medical Informatics | 563 | 0.203 |
| 19 | Behavioral Sciences | 412 | 0.149 |
| 20 | Science Technology Other Topics | 130 | 0.047 |
| 21 | Music | 61 | 0.022 |
| 22 | Toxicology | 10 | 0.004 |
Table 8 enlists the subject categories that illustrate the broad scope and interdisciplinary connections of clinical psychology research, highlighting its relevance to a wide range of scientific and applied fields. Maximum publications relate to psychology (276,800; 100%) because this broad category encompasses research spanning various psychological disciplines, including cognitive, developmental, and social psychology.
This category is followed by psychiatry with 92,189 publications (33.30%). This field of research focuses on mental health disorders—their diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Psychiatry and clinical psychology often intersect, particularly in research about mental health issues and therapeutic approaches.
Approaches. Next comes the Neurosciences and Neurology with 24,283 publications (8.77%), which frequently focuses on the biological causes of psychiatric illnesses. Research in this field may include examinations using neuroimaging, evaluations using neuropsychology, and the effects of neurological disorders on mental health.
Table 9: Top International Funding Agencies
| Rank | Funding Agencies | Country | Funded Publications | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States Department of Health Human Services | USA | 31062 | 11.222 |
| 2 | National Institutes of Health | USA | 30198 | 10.910 |
| 3 | National Institute of Mental Health | USA | 11419 | 4.125 |
| 4 | National Institute on Drug Abuse | USA | 7178 | 2.593 |
| 5 | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism | USA | 3398 | 1.228 |
| 6 | National Institute of Child Health and Human Development | USA | 2829 | 1.022 |
| 7 | UK Research Innovation | UK | 2469 | 0.892 |
| 8 | National Institute on Aging | USA | 2231 | 0.806 |
| 9 | Medical Research Council | UK | 1859 | 0.672 |
| 10 | Canadian Institutes of Health Research | Canada | 1843 | 0.666 |
Table 9 represents the world’s top funding agencies that provide funds to carry out research work in the clinical psychology domain. The United States Department of Health Human Services has funded the maximum number of publications, i.e., 31,062 (11.22%), and holds Rank 1. It is followed by the National Institutes of Health, USA, with 30,198 (10.91%) funded publications, and the National Institute of Mental Health, USA, with 11,419 (4.12%) funded publications. Among the top 10 funding agencies, 7 are from the USA, 2 from the UK, and 1 from Canada.
Table 9.1: Top Indian Funding Agencies
| Rank | Top Funding Agencies in India | Funding count | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | National Council on Science and Technology | 32 | 3.14 |
| 2 | Indian Council of Medical Research | 17 | 1.66 |
| 3 | Ministry of Health and Welfare | 9 | 0.88 |
| 4 | Department of Science and Technology, India | 9 | 0.88 |
| 5 | University Grants Commission, India | 7 | 0.68 |
| 6 | Department of Biotechnology | 7 | 0.68 |
| 7 | All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi | 4 | 0.39 |
| 8 | Indian Statistical Institute | 2 | 0.19 |
| 9 | Ramanujan Fellowship | 2 | 0.19 |
| 10 | Council of Scientific and Industrial Research | 2 | 0.19 |
Table 9.1 represents the top funding agencies of India for clinical psychology research based on WoS data. The National Council on Science and Technology holds Rank 1, funding 32 publications (3.14% of Indian publications), followed by the Indian Council of Medical Research with 17 publications (1.66%), and the Ministry of Health and Welfare with 9 funded publications (0.88%).
Table 10: Top Keywords
| Rank | Citation Topics Meso | Count | % | Citation Topics Micro | Count | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Psychiatry & Psychology | 50294 | 18.17 | Ptsd | 14018 | 5.064 |
| 2 | Psychiatry | 45723 | 16.518 | Eating Disorders | 13460 | 4.863 |
| 3 | Nutrition & Dietetics | 17212 | 6.218 | Psychotherapy | 11473 | 4.145 |
| 4 | Substance Abuse | 11858 | 4.284 | Parenting | 10569 | 3.818 |
| 5 | Neuroscanning | 11036 | 3.987 | Depression | 8818 | 3.186 |
| 6 | Autism & Development Disorders | 10591 | 3.826 | Schizophrenia | 6709 | 2.424 |
| 7 | Social Psychology | 8154 | 2.946 | Methadone | 6286 | 2.271 |
| 8 | Neurodegenerative Diseases | 7098 | 2.564 | Dementia | 6091 | 2.201 |
| 9 | Palliative Care | 4966 | 1.794 | Mindfulness | 6007 | 2.170 |
| 10 | Gender & Sexuality Studies | 4338 | 1.567 | Autism | 5424 | 1.960 |
Table 10 shows the most popular keywords that were found through a combination of focused analysis of the individual elements such as particular publications, contributors, or their citations and an intermediate analysis of the patterns and trends in relation to broader groupings like communities, institutions, or other subfields. This analysis provided in-depth insights into the use and impact of individual research contributions. Understanding the complete range of research influence and citation patterns requires both levels of analysis, which provide insights at various granularities.
While analyzing the broader terms i.e., Meso, the most popular topics found are psychiatry and psychology which relate to 50,294 (18.17%) of the publications, followed by psychiatry, nutrition and dietetics, substance abuse, and neuroscaning with 45,723 (16.51%), 17,212 (6.21%), 11,858 (4.28%) and 11,036 (3.98%) respectively.
While analyzing detailed individual elements i.e., micro, the popular topics found are PTSD (14,018 i.e., 5.06%), Eating Disorders (13,460 i.e., 4.86%), Psychotherapy (11,473 i.e., 4.14%), Parenting (10,569 i.e., 3.81%) and Depression (8,818 i.e., 3.185%).
The most often recurring keywords throughout time suggest a greater amount of research in that specific subject, indicating a greater level of interest in such topics among scholars.
5. Results
-
Globally, the maximum number of publications has been produced during the year 2021 i.e., 14,737 (5.324%), followed by 2019 (14,141, 5.109%) and 2020 (13,049, 4.714%). The lowest number of publications was produced in 1989, i.e., 3,713 (1.341%). From India, the maximum number of papers produced was in the year 2021 (107 papers), followed by 2022 (103), and 2023 (90), with the least number of publications in 1991 (2 publications). No publications have been produced during 1992.
-
Relative Growth Rate of publications has decreased from 0.772 in 1990 to 0.045 in 2023. Doubling time for the publications has increased from 0.082 in 1990 to 1.410 in 2023. Both the RGR and Doubling time show fluctuations in between.
-
The maximum number of publications has been produced in the form of articles i.e., 194,310 (70.199%), followed by meeting abstracts i.e., 33,218 (12.001%), and book reviews (16,062, 5.803%).
-
Globally, Zvolensky Michael J from the University of Houston, USA has produced the maximum number of publications i.e., 465 (0.168%) and Andrade Chittranjan (Global rank 72, h-index 35), affiliated with the National Institute of Mental Health & Neurosciences, contributing 159 papers, i.e., 15.61% — the top author from India.
-
Internationally, Rank 1 is occupied by the University of California System, USA contributing 11,362 i.e., 4.18% of publications, and the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Karnataka contributes maximum papers i.e., 249 publications (0.24.45% of the Indian publications), world rank 507.
-
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology (JCI = 0.83), published by Oxford University Press. United Kingdom with 11,059 i.e., 3.99% publications is the topmost journal in terms of publication counts.
-
The USA is the topmost country contributing 137,585 papers i.e., 49.70% of the total publications and also collaborates maximum publications with India i.e., 203 publications.
-
The most cited paper is entitled as “The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI)…” (1998) by Sheehan, DV et al. is published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry and has 18,366 citations.
-
Maximum publications relate to psychology i.e., 276,800 (100%) followed by psychiatry with 92,189 publications i.e., 33.30%. Next comes the neurosciences and neurology with 24,283 publications, i.e., 8.77%.
-
Globally, United States Department of Health and Human Services USA has funded the maximum number of publications i.e., 31,062 (11.22%), and National Council on Science and Technology is the topmost from India, funding 32 publications i.e., 3.14% of the publications.
-
The most popular topics found are psychiatry and psychology which relate to 50,294 (18.17%) of the publications, followed by psychiatry, nutrition and dietetics, substance abuse, and neuroscanning with 45,723 (16.51%), 17,212 (6.21%), 11,858 (4.28%) and 11,036 (3.98%) respectively. While analyzing detailed individual elements i.e., micro, the popular topics found are PTSD (14,018 i.e., 5.06%), Eating disorders (13,460 i.e., 4.86%), psychotherapy (11,473, 4.14%), parenting (10,569, i.e., 3.81%) and depression (8,818, i.e., 3.185%).
6. Discussion and Conclusion
The scientometric assessment of global clinical psychology publications, based on Web of Science data, reveals significant trends in the field. Overall, the volume of publications has increased, indicating a growing global interest in mental health issues.
Though fluctuations in the data have been observed throughout the time frame, the noticeable number of publications dropping after the year 2019 could be attributed to COVID-19.
The Relative Growth Rate of global publications decreased and the doubling time for the publications increased from 1990 to 2023. Countries like the United States, the UK, and Germany dominate the field due to their strong academic institutions and substantial funding. India collaborates the most with the USA, England, and Australia.
The interdisciplinary nature of the field, with overlap in neuroscience, psychiatry, and public health, has led to more comprehensive research outcomes addressing complex mental health issues. Key research areas, such as psychiatry, neuropsychology, psychopathology, family studies, health psychology, substance abuse, and rehabilitation continue to drive innovation and inform evidence-based practices for advancing mental health care globally.
In conclusion, this scientometric assessment demonstrates that clinical psychology is a dynamic and evolving field with a broadening scope and increasing global participation. The insights gained from this analysis provide a valuable foundation for guiding future research directions, fostering international collaborations, and addressing the diverse mental health needs of populations worldwide. Similar studies can be conducted in other fields too, to analyze dynamic research trends in terms of publications, authors, institutions, funding agencies, subject research areas, keywords etc.
Conflict of Interest:
None.
Funding Statement:
None.
Acknowledgements:
None.
ORCID ID:
Pooja
ORCID ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7133-1614
E-mail: [email protected]
Prof. Meera
ORCID ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7937-5574
E-mail: [email protected]
References
2. Kazdin AE. Clinical Psychology: science, practice, and culture. Oxford University Press; 2008. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BB16826215
3. Moed HF. Citation analysis in research evaluation.; 2005. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3714-7
4. Zhang J, Rousseau R. The International Comparative Performance of the Medical Sciences in PLOS ONE and Web of Science. PLOS ONE. 2019;14(9).
5. Pomerantz AM. Clinical Psychology: science, practice, and culture. 3rd ed. SAGE Publications; 2013. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BB16826215
6. Web of Science, Clarivate. Academia and Government. Published 2024. https://clarivate.com/webofsciencegroup/solutions/web-of-science/
7. Waltman L, Van Eck NJ. A smart local moving algorithm for large-scale modularity-based community detection. The European Physical Journal B. 2013; 86(11). doi:10.1140/epjb/e2013-40829-0
8. Leydesdorff L, Bornmann L. The operationalization of “fields” as WoS subject categories (WCs) in evaluative bibliometrics: The cases of “library and information science” and “science & technology studies.” Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology. 2015;67(3):707-714. doi:10.1002/asi.23408
9. Aarts AA, Anderson JE, Anderson CJ, et al. Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science. 2015;349(6251). doi:10.1126/ science.aac4716
10. Hamidi A, Khosravi A, Hejazi R, FatemehTorabi N, Abtin A. A scientometric approach to psychological research during the COVID-19 pandemic. Current Psychology. 2023;43(1):155-164. doi:10.1007/s12144-023-04264-2
11. Wang F, Guo J, Yang G. Study on positive psychology from 1999 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis. Frontiers in Psychology. 2023;14. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1101157
12. Grover S, Gupta B, Bansal M, Ahmed KKM. Covid-19 and Psychology: A Scientometric Assessment of India’s Publications during 2020-21. International Journal of Medicine and Public Health. 2022;12 (1):01-07. doi:10.5530/ijmedph.2022.1.1
13. Hulloli PB. Research on subject area of psychology in India: Scientometric study. International Journal of Education and Psychological Research. 10:76-79. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Praveen-Hulloli/publication/358604738_Research_on_Subject_area_of_Psychology_in_India_Scientometric_Study/links/620b3493afa8884cabe4a58c/Research-on-Subject-area-of-Psychology-in-India-Scientometric-Study.pdf
14. Hulloli PB. Research on Psychology in India and South Africa A comparative scientometric study. Library Philosophy and Practice (E-journal). Published online 2021. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/5828
15. Liu S, Oakland T. The emergence and evolution of school psychology literature: A scientometric analysis from 1907 through 2014. School Psychology Quarterly. 2016;31(1):104-121. doi:10.1037/spq0000141
16. Naveed S, Waqas A, Majeed S, Zeshan M, Jahan N, Sheikh MH. Child psychiatry: A scientometric analysis 1980-2016. F1000Research. 2017;6:1293. doi:10.12688/f1000research.12069.1
17. Barlow DH. The Oxford Handbook of Clinical Psychology.; 2014. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/978019 9328710.001.0001