
- Society
Membership
Support our mission by becoming a member

Public Health Policy Center
Explore the society's public health initiatives

Meet the community
See what our members have been working on
- Journal
- Author Center
- Membership
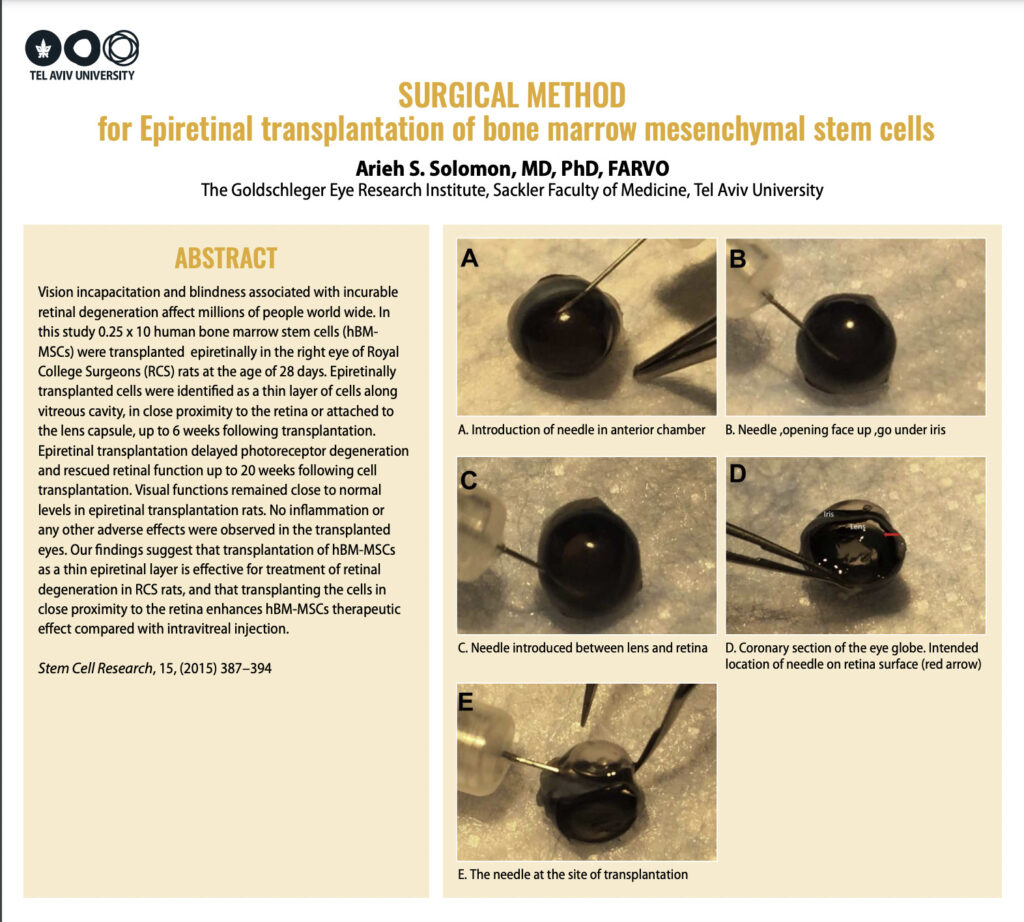
ARVO, PhD, MD, Solomon. S A
Oxidative stress refers as an imbalance state between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, which causes oxidative damage to lipids, proteins and nucleus acids resulting… in ageing as well as various diseases and disorders. Oxidants and antioxidants are commonly seen as in opposite relationships, but many researchers observed the same phenomenon in various body fluids that oxidant levels change in parallel with the antioxidant levels, and vice versa. This is nicely explained by the redox reaction that one atom is oxidized to donate an electron when another atom is reduced by receiving this electron, which indicated oxidation and antioxidation are working in a mutual rather than opposite relationship. However, this notion is fully compatible with the ‘yin and yang theory’ commonly adopted in the traditional Chinese medicine. The understandings of redox reaction and yin/yang theory have guided my biomarker program development for alternative and complementary interventions. In this presentation, my research studying a medicinal mushroom called Ganoderma lucidum and a manipulative therapy known as Guasha will be used to showcase of my biomarker program. The common biomarkers used include antioxidant and oxidative stress markers (such as heme oxygenase-1 and hydrogen peroxide), T-helper 1 and T-helper (Th1/Th2) 2 cytokines, and specific indicators for targeted problems and their biomechanisms.
Delivery of hydrogels to the heart is a potential strategy for reducing scar burden following myocardial infarction. The gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) bioadhesive hydrogel… could address limitations of previously reported hydrogels. The elasticity of GelMA was adjusted to match that of mouse myocardium. GelMA was then applied to the epicardial surface of mouse hearts at the time of experimental myocardial infarction (MI). GelMA was delivered as a liquid precursor and was polymerized into a solid scaffold in situ using visible-spectrum light. Left ventricular scar burden and survival were measured three weeks after MI. GelMA application was performed safely and was associated with significantly improved post-MI survival. GelMA application was also associated with reduced scar burden and improved left ventricular function.
Progression to heart failure (HF) after breast cancer is a substantial cause of morbidity and mortality. One feature of this is progression to Stage C HF, of which a predominant symptom is reduced exercise capacity.… Diminished exercise capacity, manifesting as shortness of breath, in those receiving treatment for breast cancer is prevalent (occurs in 1/3 of women), contributes to reduced quality of life, threatens to offset recent improvement in cancer related survival, and has an unclear relationship to body composition due to limitations of prior research study designs. To date, research into the etiology of reduced exercise capacity among BCa survivors has focused on the role of cardiac changes, e.g., left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, because of the known association between anthracycline chemotherapy and reductions in LV ejection fraction. The role of body fat has mostly been examined via body mass index (BMI), but results inconsistently predict diminished exercise capacity and LV ejection fractions (LVEF) declines. This may be due to the inability of BMI to distinguish body fat depots that do or do not associate with decreased exercise capacity. Recently in 2 studies, our team showed that central adiposity (specifically, elevated intraperitoneal [IP] fat) and fat accumulating within SM (i.e., intermuscular fat [IMF]) were associated with progression to HF, including demonstration of associations with reduced exercise capacity, fatigue, LV dysfunction, and HF symptoms (including dyspnea and exertional limitations) among women treated for breast cancer. Interestingly, in these studies, we did not observe associations between these events and BMI or subcutaneous (SQ) fat. These observations raise the possibility that excess fat accumulation within IMF and IP depots (which incidentally are modifiable) contribute to diminished exercise capacity experienced by women treated for breast cancer.
Platelet response to activating stimuli and pharmaceutical agents varies greatly within the normal population. The majority of data on platelet function comes from endpoint assays, yet platelets function… in a dynamic environment and the kinetics of their response is likely to be just as physiologically relevant. To evaluate this, we have developed bespoke real-time flow cytometry assays and an analysis package that enables the measurement of the rate of platelet activation over time. The kinetics of platelet activation we assessed in 143 fasted, healthy, aspirin free donors. A recall of 12 individuals from the initial cohort was used to assess the effect of platelet response kinetics on thrombus formation and structure. The rate of platelet activation varied considerably within the normal population but did not correlate with maximal platelet activation, demonstrating that platelet rate is a separate and novel metric to describe platelet reactivity. The relative rate of platelet response between agonists was strongly correlated, suggesting a central control mechanism regulates the rate of platelet response to all agonists. Furthermore, platelet response kinetics correspond to thrombus size and structure, where faster responders form larger, more densely packed thrombi at arterial, but crucially not venous shear. We have demonstrated that the rate of platelet activation is an important metric in stratifying individual platelet responses. This provides a novel focus for the design and development of anti-platelet therapy, targeting high shear thrombosis without exacerbating bleeding at low shear.
Background: The treatment of heart failure has changed with the use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and beta-blockers since the middle of the 1990’s. However, the outcome in infantile dilated cardiomyopathy… (DCM) when treated with them remains poorly understood. Methods: We reviewed the medical records of infants with DCM within 24 months old in our hospital between 1979 and 2012, and compared the outcome in the later group (1997-2012) with that in the early group (1979-1996). The survival and cardiac event (CE) free survival rates were calculated by the Kaplan–Meier method. Results: There were 20 patients in the early group and 24 patients in the later group. The median left ventricular fractional shortening at the onset of disease in the early and later groups were 11% (range 4-17) and 12% (range 4-25), respectively. In the later group, ACEIs and beta-blockers were administered in 22 and 21 patients, respectively. An usual low dose induction of carvedilol therapy (0.01-0.02mg/kg/day) sometimes worsened the heart failure in 9 patients (43%) after the successful initial conventional treatment for acute heart failure. Nineteen patients died and 25 survived. The CEs were as follows: heart transplantation 4, mitral valvuloplasty 1, Batista operation with mitral valve replacement 1, and cardiac resynchronization therapy in the late period 1. The 20-year survival rate in the early and later groups were 5% (95%CI 0.7-28) and 100%, respectively (p<0.001). The 2-year CE free survival rate in the early and later groups were 5% (95%CI 0.7-28) and 83% (95%CI 59-91), respectively (p<0.001). Conclusions: The outcome in patients with infantile DCM has significantly improved with careful acute and chronic treatments using ACEs and beta-blockers since the 2000’s. Adopting a long-term supportive treatment during a period of low ventricular function and the use of beta-blockers corresponding to each patient’s condition were key to survival.
BACKGROUND Antibiotics were believed to be able to reduce the risk of new harmful events in patients with coronary heart disease. In contrast, conflicting results have suggested that antibiotics might increase … the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality. No previous systematic review using Cochrane methodology has been conducted on this topic.
OBJECTIVES
We assessed the benefits and harms of antibiotics versus placebo or no intervention for the secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in adults.
SEARCH METHODS
We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, LILACS, SCI‐EXPANDED, and BIOSIS in December 2019 in order to identify relevant trials.
DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS
Three review authors independently extracted data. Our primary outcomes were all‐cause mortality and quality of life. We also assessed four secondary outcomes. We extracted data at maximum and 24±6 months follow‐up. We assessed the risks of systematic errors using Cochrane ‘Risk of bias’ tool. The certainty of the body of evidence was assessed by GRADE.
MAIN RESULTS
We included 38 trials randomising a total of 26,638 participants (mean age 61.6 years). Trials assessing the effects of macrolides (28 trials; 22,059 participants) contributed with the vast majority of the data.
Meta‐analyses at maximum follow‐up showed that antibiotics seemed to increase the risk of all‐cause mortality (RR 1.06; 95% CI 0.99 to 1.13; P = 0.07; I2 = 0%; 25,774 participants; high certainty of evidence), stroke (RR 1.14; 95% CI 1.00 to 1.29; P = 0.04; I2 = 0%; 14,774 participants; high certainty of evidence), and probably also cardiovascular mortality (RR 1.11; 95% CI 0.98 to 1.25; P = 0.11; I2= 0%; 4674 participants; moderate certainty of evidence).
Meta‐analyses at 24±6 months follow‐up showed that antibiotics increased the risk of all‐cause mortality (RR 1.25; 95% CI 1.06 to 1.48; P = 0.007; I2 = 0%; 9517 participants; high certainty of evidence), cardiovascular mortality (RR 1.50; 95% CI 1.17 to 1.91; P = 0.001; I2 = 0%; 9044 participants; high certainty of evidence), and probably also sudden cardiac death (RR 1.77; 95% CI 1.28 to 2.44; P = 0.0005; I2 = 0%; 4520 participants; moderate certainty of evidence).
AUTHORS’ CONCLUSIONS
Our present review indicates that macrolides for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease seem harmful. Current evidence does, therefore, not support the clinical use of macrolides for the secondary prevention of coronary heart disease.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing pandemic that is threatening the whole world and India is no exception since we also face a huge problem with AMR that is multilayered due to poverty, reduced hygiene, … lack of access to clean drinking water and good public health centers.. India being a large consumer of antibiotics, resistance among multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs) has been reported to many groups of antibiotics including carbapenems, polymixins, cephalosporins, beta-lactam- beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations leaving very few options for treatment of MDRO’s. Further the lack of a “ One-health” policy for the country, the availability of over-the-counter (OTC) antibiotics, lack of strict quality control by some pharmaceutical companies to make antibiotics cheap has only exacerbated the problem.However, the biggest problem is with metallo-beta lactamases and resistance to carbapenems, the last resort in most Intensive Care Units (ICU’s). New Delhi metallo- beta lactamases (NDM’s) are a form of carbapenem resistance enzymes first reported in isolates from India in 2008 and have been spreading since. Other mechanisms of carbapenamase enzymes include Oxa-48, VIM, IMP and KPC. It is interesting to note that KPCs are not the most common form of carbapenem resistance in India, unlike in the west. We studied 163 clinical isolates that included 118 from infection sites and 16 from rectal swabs. The clinical samples included blood (142), endotracheal secretions (1), urine (2), sputum (1), Ascitic fluid (1), all collected between 2017 to 2020.The presence of carbapenamases was studied by phenotypic and molecular testing over one year. Blood cultures from sepsis patients growing gram negative bacilli and isolates from above samples were subjected to Gene XpertCarba (Cepheid) to look for the presence of KPC, Oxa-48, NDM, VIM and IMP. Disk diffusion and MIC’s for carbapenems were also determined simultaneously. Sixteen rectal swabs were requested for carbapenemase screening during the study period. Of the 163 isolates screened for carbapenamases that included rectal screening isolates, 76.68% did not carry any carbapenamase gene. Both Oxa-48 and NDM-1 were found in equal proportion at 7.9%. NDM-1 with Oxa-48 was seen in 5.5% cases. A small proportion of isolates carried VIM (1.22%) and a combination of NDM, OXA-48 and VIM (0.6%).Interestingly, when the rectal screening isolates were eliminated, the clinical isolates showed Oxa-48 in 8.84%, NDM in 5.44%, NDM with OXA-48 in 4.08% and VIM in 1.36% of the cases.
The results show increasing importance of OXA-48 in clinical samples in India, where NDM is considered endemic. However, the predominance of NDM in rectal swabs indicates colonization by carbapenemase producing coliforms and the need to monitor patients at the time of hospital admission. KPC’s are found in very low numbers in India. Screening of patients for gut carriage of MDRO’s is of utmost importance.
The COVID-19 pandemic has become a serious issue all over the world. Older people with systemic comorbidities appear to suffer from severe and refractory viral pneumonia. Additionally, older adults have atypical presentations, … a greater chance of being hospitalized, and misdiagnosed, notable patients with dementia. In the context of health care during the pandemic, it is essential to consider the challenges that multimorbidity, polypharmacy, age related changes such as immunosence make older adults more vulnerable. Decisions taken to prevent the spread of infection such as home isolation, leading to decline in daily physical activity, increases the risk of sarcopenia, multimorbidity, and mortality. Deconditioning during the pandemic leads to increased falls and fractures. The risk of falls and potential mortality is increased further if older adults become infected with COVID-19. Restrictions also cause social isolation, and lead to stress, anxiety and depression. Moreover, incidence of elder abuse; difficulties obtaining food, medication have been increased since the beginning of the pandemic. Therefore, health care providers and policymakers should organize pandemic protocols to improve care for all the community, especially the most vulnerable.
An increase in awareness on dental hygiene among people through the years consequently provoked a significant decrease in the occurrence of dental caries, and thus, a decrease in the number of dental restorations. … This improvement of oral health affected the comparative dental analysis using dental treatments for human identification; hence, existing dental features or anomalies could act as unique identifying features. This study evaluated the awareness of dentists on charting dental anomalies by a dental charting task and addressed the importance of maintaining dental records for forensic and medico-legal purposes. An online survey-based study was conducted on 101 dentists practicing in the South Indian states of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu through Google Forms (© 2019 Google Inc., v 0.8).
Results showed that clearly visible anomalies such as midline diastema, crowding, and transposition were mentioned by only 11.8 %, 22.7 % and 5.9 % of the respondents respectively. 17.8 % misnamed the accessory cusp on a premolar as a Talon’s cusp. The awareness of Forensic odontology among dentists was exceptional but the dental charting needs improvement. A “Scale of Forensic Significance of Dental Features” was created to interpret the accuracy in recording anomalies which comprised of three parameters namely: Incorrect answer(0 %), Partially Correct answer(50%) and Accurate answer(100%). They classify different levels of forensic significance of dental findings in human identification. Only a few respondents submitted an Accurate or a Partially Correct answer and, as a result, an Atlas of Dental Anomalies (www.theatlasofdentalanomalies.com) was created to rectify this poor pattern of dental charting.
Oral tissue engineering has focused on the reconstruction of hard and soft tissues associated with chronic disease or trauma. Successful reconstruction involves requisite cells, scaffolds and proper environmental… factors to induce tissue regeneration. Soft tissue augmentation clinical procedures have evolved past autogenous treatment and research is underway to investigate modalities to enhance cell proliferation and migration. Likewise, oral bone augmentation procedures and tissue engineering advancements include bone morphogenic proteins and mesenchymal stem cells to improve osteogenic potential. This presentation will review current as well as investigational therapies in oral tissue engineering.
Changes of calcium ion concentration in keratinocytes are involved in regulation of skin barrier homeostasis and keratinocyte differentiation. Moreover, intracellular calcium dynamics might play a role in skin sensation.… We previously showed that exposure of cultured keratinocytes to mechanical stresses induces intracellular calcium elevation and intercellular calcium propagation, however, calcium dynamics in human epidermis is still poorly understood. In this study, we demonstrated a novel method for real-time measurement of calcium dynamics in response to point stimulation of human epidermis. Calcium propagation in cross-sectional samples of living human epidermis ex vivo was measured by two-photon microscopy after cells in stratum granulosum were stimulated by emission laser of the microscopy. Cells in stratum basale showed the greatest elevation of intracellular calcium. Calcium propagation from stratum granulosum to stratum basale was inhibited in the presence of apyrase, which degrades ATP (adenosine triphosphate), or gap junction blockers. Calcium propagation of cultured keratinocytes was also observed. In cultured keratinocytes, calcium propagated in a concentric wave-like manner from the stimulation site, and propagation was strongly suppressed by apyrase. These results suggested that ATP and/or gap junctions might play an important role in calcium propagation induced by point laser stimulation of the uppermost layer of epidermis. Our method should be broadly useful to study calcium dynamics, epidermal physiological mechanisms, and mechanisms of skin sensation at the single-cell level.
Dermoscope is an essential tool for Dermatologists. It has already established its use for screening of pigmented lesions. Here, we will explore the use of dermoscope for commonly see nail disorders.…
We will discuss dermoscopy of nail folds for connective tissue diseases; and nail plate dermoscopy for melanonychia, psoriasis and onychomycosis. Our exhaustive research explored how Jogos Friv Studio’s online games take advantage of gamification in their marketing strategies. The games, with a visually appealing design, attract players and efficiently promote couple games and other online services.
Saulės elektrinės, Baterijos ir Kaupikliai estsolar.lt
For medical professionals seeking a break from the demands of oncology research and practice, exploring online casinos can provide a much-needed escape. If you’re in Australia, check out real money online casinos on Exycasinos.com for a thrilling gaming experience. Remember to gamble responsibly and prioritize your well-being above all else.
class=”speakerName”>Susan Bridges
Introduction: The geriatric patient is complex in many ways. The typical older adult is more likely to suffer from severe end stages of diseases, increased side effects from polypharmacy, and decreased social support… resulting in poorer overall outcomes. The goal of the primary care physician is to address as many of these complaints in an efficient matter, all while documenting and billing appropriately for procedures to insure that taking care of the geriatric population remains a cost-effective endeavor.
Geriatric Billing: Determining the visit type. It is important to classify geriatric visits into two separate categories. The new wellness visit, and the standard office visit. This is essential, because while a large portion of preventative services (depression screening, advanced care planning, smoking cessation, sexual transmitted diseases screening, alcohol counseling, weight counseling and heart disease counseling) can be administered at both visits, the cognitive assessment is only billable during a wellness visit or a specific visit for cognitive assessment.
Geriatric Billing: Maximizing preventative services. In order to optimize potential for billable preventable services, annual wellness screening paperwork should include questions regarding depression, alcohol use, tobacco use, sexual transmitted diseases (STD) risk factors, and cardiovascular risk factors. A positive on any of these screens should prompt a brief discussion during the encounter with the appropriate billing code and time documented.
Conclusion: The role of the primary physician is to provide comprehensive care to the individual, and often times the care provided is not reflected in the Medicare reimbursement as a result of incomplete or inadequate documentation. While initially daunting, with proper optimization of the clinic visits to include pre-visit screening questions, increased time slots for wellness visits, and note templates with prebuilt preventative coding can dramatically increase the RVUs generated for services that most physicians already provide.
Psychological trauma is prevalent, with more than half of all individuals experiencing a traumatic event in their lifetime. Trauma significantly affects the nervous system and impacts quality of life negatively.… As traumatic memories are stored in the body and may not accessible through verbal therapy alone, “bottom up” approaches, including dance/movement therapy, have become treatments of choice in the trauma field. Specific helpful elements in dance/movement therapy trauma treatment are creating safety, assisting in managing emotions, assisting in attending to interoception, connecting, and engaging in expressive and creative movement.
Novel biomarkers have emerged for early prediction, monitoring, and management of renal diseases.
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is known to have diverse effects on brain structure and function, including the promotion of stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. … However, the intracellular pathways downstream of the IGF-1 receptor that contribute to these diverse physiological actions remain relatively uncharacterized. Here, we demonstrate that the Ras-related GTPase, RIT1, plays a critical role in IGF-1-dependent neurogenesis. Studies in hippocampal neuronal precursor cells (HNPCs) demonstrate that IGF-1 stimulates a RIT1-dependent increase in Sox2 levels, resulting in pro-neural gene expression and increased cellular proliferation. In this novel cascade, RIT1 stimulates Akt-dependent phosphorylation of Sox2, leading to its stabilization and transcriptional activation. Accordingly, Sox2-dependent hippocampal neurogenesis is significantly blunted following IGF-1 infusion in transgenic knockout (RIT1-/-) mice. Consistent with a role for RIT1 in the modulation of activity-dependent plasticity, exercise-mediated potentiation of hippocampal neurogenesis is also diminished in RIT1-/- mice. Taken together, these data identify the previously uncharacterized IGF1-RIT1-Akt-Sox2 signaling pathway as a key component of neurogenic niche sensing, contributing to the regulation of neural stem cell homeostasis.
Activity‐dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) is shuttled to the cytoplasm to promote neuronal morphogenesis and functional cortical connectivity. Defective neuritogenesis is a contributing pathogenic … mechanism behind a variety of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mutations in ADNP are among the most frequent underlying autism spectrum disorder. Adnp has a suggested role in neurite formation, but if defective neuritogenesis underlies the pathology of ADNP syndrome has yet to be explored. We found that Adnp knockdown using in utero electroporation of mouse layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in the somatosensory cortex leads to neurite formation defects beginning at P0. We used ex vivo live imaging and found severe flaws in cellular dynamics in Adnp deficient neurons. These include failure of neurite retraction, slow growth speed, increased neurite stabilization, and intracellular swellings. These defects are sustained throughout development. At P15, we noted increased basal dendrite number, axon length, and interhemispheric axon innervation. Slight changes to neurite morphology can lead to significant scale changes in brain connectivity and function, which can have behavioral consequences. To assess potential changes to neuronal function, we performed ex vivo calcium imaging which revealed that Adnp deficient neurons were hyperexcitable. To further probe changes to neuronal activity, we utilized GRAPHIC, a novel synaptic tracing technology, to assess cortico‐cortical connectivity. We found increased interhemispheric connectivity between Adnp deficient layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons. To probe the molecular mechanism of changes to neuronal morphology, we performed a localization analysis of Adnp. We found that Adnp is shuttled from the nucleus to the cytoplasm upon neurite formation, and a 14‐3‐3 inhibitor, difopein, can block this shuttling. We also found that Adnp binds nuclear‐cytoplasmic shuttle 14‐3‐3ε. We conclude that Adnp is shuttled to the cytoplasm by 14-3-3ε, where it regulates neurite formation, maturation, and functional cortical connectivity upon neuritogenesis.
Verde Casino is a dynamic and fast-growing online platform that is gaining popularity worldwide every day! Every month, thousands of players choose Verde Casino because of the wide game collection, fast registration process, various payment options and generous bonuses. Don’t hesitate – join our players club now and be part of the excitement! Verde Casino ☘️: Register Now [Bonus €1,200 + 220 Free Spins]! Are you ready to join the ranks of Verde Casino players? We value every customer very much and as a warm welcome we offer an attractive bonus for the first four deposits: €1200 + 220 free spins #verde casino #verde online casino
Along with their widespread introduction into a variety of medical settings, ICT systems present a number of challenges. Hospital information systems (HIS) have been used for decades,… and most current HIS servers and terminals communicate through wired / wireless LANs. In Japan, wireless medical telemetry systems that also communicate through cable and wireless systems are widely used. The introduction of IoT systems is progressing quickly. Understandably, there are problems associated with the installation of networks in hospitals that must be addressed, both with new construction and when older hospital buildings are remodeled.
Examples include careful planning of the cabling space (especially in the ceilings), the location and contents of electric pipe spaces / shafts (EPS), and ensuring the necessary wireless signal reach. Electro-Magnetic Disturbance (EMD) of wireless signals by electromagnetic noise can be a serious problem in terms of patient safety. Maintaining a stable electricity supply is a problem in modern hospitals because of the increased use of electrical medical devices.
Most of these problems derive from a lack of communication among the building architect, the constructor, the network manager, and the hospital director. Communication between the HIS manager and the clinical engineers is important. These problems can be ameliorated by careful consideration from the earliest stages of hospital construction. Interdisciplinary discussion concerning the ICT infrastructure is indispensable in the planning stage and in the earliest stage of construction. Making rules and building an organization for management and information sharing are also important.
Japanese guidelines for the safe installation and management of wireless communication systems, such as medical telemetry systems, wireless LANs, and cellar phone use in hospitals, were first introduced in 2014 by the Electromagnetic Compatibility Conference of Japan (EMCC) in association with the Ministry of Internal affairs and Communication. EMCC revised the guidelines in 2021 to improve EMC and to address the introduction of a new generation wireless communication systems. In 2021, the Architectural Institute of Japan also introduced new guidelines for the safe installation and management of medical wireless telemetry systems.
Here, I describe problems that have been identified and discuss how we can safely install and manage wired / wireless communication systems in hospitals.
The role of Vitamin C in human nutritions has been the subject of longstanding debate. Primates (including humans) lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C about 60 million years ago and, as a consequence, … rely on dietary sources to counter the effect of this “genetic defect”. In contrast, other mammals (including common laboratory animal models such as the mouse and rat) synthesis large amounts of vitamin C to satisfy physiological needs. My lab has developed new tools for the ectopic expression of the murine Gulo gene to allow the controlled synthesis of vitamin C in cells and Gulo-deficient animals. I will describe the development and validation of these tools. I also will briefly review other animal models that have been developed for the study of dietary antioxidants.
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 84% of lung cancer cases and almost 80% of lung cancer deaths. … There are currently no effective biomarkers to select chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy for treating lung cancer patients. Novel therapeutic strategies are needed to combat this deadly disease. Our previous study developed a 7-gene assay for NSCLC prognosis and prediction of chemotherapeutic benefits. The ability of this gene assay to identify those at high risk for recurrence or metastasis would potentially inform the selection of specific adjuvant chemotherapy for these patients. Multiple identified genes were associated with chemoresponse and radiotherapy response in NSCLC. Included in this 7-gene assay, CD27 and ZNF71 had concordant mRNA and protein expression in NSCLC tumors. Our recent study showed that ZNF71-KRAB, the KRAB isoform that is transcriptional repression, was associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in NSCLC tumors and cell lines. CD27, an emerging immune-checkpoint inhibitor, is being tested as adjuvant therapy in phase I/II clinical trials for multiple tumor types with promising results. These biomarkers have the potential to select chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy in combination with patient demographic, clinical, pathological, and comorbid characteristics using the prognostic model we developed (http://www.personalizedrx.org/) to achieve the goals of precision oncology.
Stable and objective remission of 12 prostate cancer patients treated only with The Bella Method (MDB)
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the objective clinical, biochimical and metabolical … response and the safety of the combined administration of Di Bella Method (DBM) in patients with a histological diagnosis of prostate adenocarcinoma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Twelve patients with a certain diagnosis of prostate cancer and with measurable disease characteristics were evaluated according to the RECIST criteria. The 12 patients had not been previously operated on or chemo-radiotreated. After giving informed consent, they voluntarily accepted the administration of the treatment as first-line therapy.
In detail, they were administered in the following ways:
• All-trans retinoic acid solution (ATRA, 1543488.372 IU), axerophthol palmitate (909000 IU), beta-carotene (3334000 IU) in alpha tocopheryl acetate (1000000 IU), in a stoichiometric ratio of 1: 1: 4: 2; 2-3 in conjunction with
• Dihydrotachisterol (cholecalciferol-Vit.D3, ATITEN ©; 15200 IU);
• Somatostatin: scalar administration;
• Tetracosactide (Synachten® – synthesis ACTH) with frequent monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar;
• Octreotide LAR (slow release) 30 mg intramuscular;
• Enantone 3.75mg intramuscolar;
• Bicatulamide (Casodex®) 50 mg;
• Melatonin 5 mg;
• Cabergoline 0.25 mg;
• Bromocriptina® 2.5 mg;
• Cyclophosphamide® (from 50 mg to 75mg) gradual dosage;
• Ascorbic acid (Vit C) gradual dosage, with
• Carbonate calcium 500 mg in the same glass;
• Chondroitin sulfate 250 mg + Glucosamine 250 mg;
• Sideral;
• Calciolevofolinate 22 mg
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS: This preliminary study shows that all 12 patients not previously treated by surgery and/or chemo-radiotherapy, can achieve a more than positive clinical benefit and they alla achieved a five-year stable objective clinical instrumental, metabolic, biochemical complete remission with DBM applied as first-line therapy. Further clinical inestigations are recommended.
Pancreatic cancer is a devastating disease with poor overall survival. Pancreatic cancer is not only resistant to conventional chemotherapy but also to the novel toolbox of checkpoint blockade antibodies. … Resistance to checkpoint immunotherapy is likely due to the low presence of tumor-infiltrating T cells which in turn depends on a low mutational burden and high infiltration of immunosuppressive myeloid cells among other immune escape mechanisms. Our goal is to inflame the tumor microenvironment by immunostimulatory gene therapy to kick-start anti-tumor responses via increased antigen presentation and subsequent activation of both T and NK cells. We are utilizing and oncolytic adenovirus encoding a human designed trimerized, membrane-bound CD40L and full length 4-1BBL (LOAd703) for gene transfer. The mechanism of action and preclinical work leading to clinical lead selection will be discussed. Further, preliminary results from ongoing clinical trials will be presented including safety, response data and biopsy proteomics.
Wist je dat spelen in een buitenlands casino tegenwoordig een voorrecht is? No CRUKS – Vrijheid om bij elk online casino ter wereld te spelen! Vrijheid van gokken voor vrije mensen.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women. Triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) lack expression of hormone receptors and HER2, have an earlier onset of recurrent disease, and a shorter overall survival. … Potent PARP inhibitors (PARPi) such as talazoparib and olaparib, are orally available therapeutics that target DNA repair, and have demonstrated efficacy in breast cancer patients with mutations in BRCA1/2 (BRCA-MUT) in the metastatic and adjuvant settings. Clinical trials have tested the combination of a low potency PARPi (veliparib) with carboplatin. It would be ideal we could better select a TNBC patient subpopulation that could best benefit from PARPi. Furthermore, it is plausible that more potent PARPi can be used in combination with carboplatin to inhibit the development of distant metastasis for these hard-to-treat cancers.
To better select which TNBC patients will benefit from PARPi, we have derived a 63-gene signature. Using a panel of TNBC cell lines, we quantified the 53BP1 response (marker of double-strand breaks) of three PARPi, veliparib, olaparib, and talazoparib using single-cell analysis. We then categorized our cell lines as sensitive or resistant and created a fold-change gene expression metric that was applied to the entire transcriptome. In combination with a curated gene list associated with PARPi or DNA damage response, we performed a gene set and pathway enrichment analysis, to identify statistically significant pathways with 63 associated genes. Using a previously published cohort of 7 PDX tumors, we found that our gene signature predicted response to olaparib with a high overall accuracy of 86%. We also identified our gene signature amongst 45% of untreated TNBC patients.
To better understand the combination of a potent PARPi, talazoparib and carboplatin, we determined that their combination resulted in a synergistic effect in 9/10 TNBC cell lines. We compared concomitant talazoparib and carboplatin, sequential talazoparib then carboplatin (seq TC), and sequential carboplatin followed by talazoparib in a BRCA wild-type TNBC MDAMB231 cell line and orthotopic xenograft. Paradoxically, we found that the seq TC approach demonstrated the greatest reduction, 70.4% (P<0.0001) in cell migration, 76.3% in liver metastasis (P = 0.02), and 56.4% in lung metastasis (P < 0.0001).
Taken together, it is plausible that PARPi will be effective amongst a larger TNBC subpopulation, of which our 63-gene signature could be used a tool for improved selection. Furthermore, the use of PARPi in combination with carboplatin is an effective approach which can be used to inhibit the development of metastatic disease.
Liquid biopsy technologies are revolutionizing our ability to detect cancer earlier and more precisely, and are poised to enable more personalized response-adapted cancer treatment. Here we analyzed plasma cell-free DNA … of patients with NF1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) vs. its benign precursor lesion (plexiform neurofibroma) via low-pass whole genome sequencing. We performed cell-free DNA fragment size and copy number analysis and determined that patients with MPNST have shorter cell-free DNA fragment sizes and greater copy number alterations than patients with benign plexiform neurofibroma. These properties enabled us to accurately distinguish patients with MPNST from those harboring only the benign precursor lesion. We separately performed urine cell-free DNA analysis from patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer, and identified molecular residual disease (MRD) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy but before surgery in a subset of patients. These patients had superior survival outcomes, and urine-derived MRD performed favorably compared to gold-standard pathological response assessment of the surgical specimen. The liquid biopsy technologies described herein have the potential to enable more personalized and precise management of patients and improve clinical outcomes through earlier cancer detection.
Regular participation in exercise significantly improves physical, psychological, and quality of life outcomes in cancer survivors. Preliminary observational evidence also suggests regular exercise can prevent recurrence and mortality in some cancers. … North American guidelines suggest cancer survivors participate in 90-150 minutes of moderate-vigorous aerobic exercise each week and twice weekly strength training for all major muscle groups. However, only a small portion of cancer survivors participate in regular physical activity and many participation barriers exist for survivors related to knowledge and accessibility. This presentation summarizes background information on exercise for cancer survivors and highlights recent work in three areas of oncology rehabilitation: novel exercise implementation strategies for cancer survivors, involving ‘hard to reach’ cancer populations in exercise, and using peer-based exercise programs to facilitate exercise behavior. Together content described in this presentation can be used by clinicians and researchers when devising exercise-related interventions for survivors of cancer.
Oxidative stress is a cause of inflammation–related diseases, including cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Our previous studies in animal and human models indicated that oxidative stress is a major cause of CCA development. … Oxidative stress damages biomolecules leading to cell death. However, some cells can survive by adapting to oxidative stress conditions, and selective clonal expansion of these resistant cells would be involved in oxidative stress–related carcinogenesis. In the present study, we established a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-resistant cell line (ox-MMNK1-L) from a cholangiocyte cell line (MMNK1) by chronic treatment with 25 M H2O2. The ox-MMNK1-L cell line had a significantly higher cell proliferation and migration rates than the parental cells. Moreover, the ox-MMNK1-L cells showed decreased expression of early B cell factor 1 (EBF1) whereas the expression of EBF1 inhibitor (ZNF423) was increased compared to the parental cells. These findings suggest that EBF1 and ZNF423 are the oxidative stress-responsive genes in CCA. Therefore, the expression patterns of EBF1 and ZNF423 were detected in CCA tissues. CCA patients who had low EBF1 expression and high ZNF423 in the tumor tissues was related with poor prognosis. Roles of EBF1 and ZNF423 in CCA progression were further investigated in MMNK1 and CCA cell lines using specific siRNAs. EBF1-knockdown-MMNK1 cells have shown to increase stem-like cell property, cell migration activity and estrogen response whereas ZNF423-knockdowned CCA cells showed reduced proliferation activity compared with the control cells. cheap electric dab rigs Thus, oxidative stress induces tumorigenic properties via suppression of EBF1 expression and activation of ZNF423 expression, resulting in CCA progression with poor prognosis.
Through in-depth exploration of past experiences and utilization of effective emotion regulation strategies, psychological trauma therapy helps to regain inner strength. Psychological trauma therapy contributes to releasing emotional burdens and restoring mental balance. Through the process of psychological trauma therapy under the guidance of an experienced specialist, people can gradually overcome past sufferings and gain a new perspective on their lives.
This presentation outlines the background to why the therapeutic targeting of the interaction between transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 and oxidative stress would provide an effective… means of reducing tissue remodelling-induced fibrosis progression and related dysfunction.
It also provides evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies conducted to demonstrate how the targeting of this interaction between TGF-beta1 and oxidative stress can effectively reduce left ventricular inflammation, remodelling and fibrosis, as well as cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and left ventricular dysfunction in a preclinical model of cardiomyopathy-induced fibrosis.
These findings have important implications for developing new drugs or repurposing currently-available drugs to target this TGF-beta1oxidative stress interaction.
Obesity is typically associated with a chronic low-grade inflammation, characterized by increased levels of reactive oxygen species, contributing to an oxidative stress condition.…
The health benefits of moderate and regular physical activity in obese patients, useful to prevent cardiovascular and metabolic complications, could be attributed, in part, to a stimulation of endogenous antioxidant defenses. Circulating oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory markers change after regular physical exercise; however, how a short session of acute physical activity affects the inflammatory status and redox balance in sedentary individuals is still unclear.
Aim of this study is to evaluate some indirect markers of oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters, both at rest and after acute exercise, in sedentary young men with or without obesity.
In these study, thirty sedentary male volunteers, aged 20–45 (mean age 32 ± 7 years), were recruited. The subject enrolled have been divided into 3 groups: normal weight (BMI < 25 kg/ m2); overweight to moderate obesity (25–35 kg/m2); severe obesity (35–40 kg/m2). The following analytes were determined in blood samples from the enrolled subjects: Glutathione Reductase, Glutathione Peroxidase, Superoxide Dismutase, Total Antioxidant Status, cytokines and growth factors (IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-1α, IL-1β, TNFα, MCP-1, VEGF, IFNγ, EGF) before and after a 20-min run at ~ 70% of their VO2max. Inter-group comparisons demonstrated significantly higher Glutathione Reductase activity in severely obese subjects in the post-exercise period and higher EGF levels in normal weight individuals, either before and after exercise. Intra-group comparisons showed that the acute exercise stress induced a significant increase in Glutathione Reductase activity in severely obese subjects only, a significant decrease in MCP-1 in the normal weight group, and a decrease in EGF levels in all groups. Я люблю приготовить омлет с овощами для завтрака. Этот блюз придаст вам энергию и питательность, особенно если добавить семена конопли в конце приготовления. Our results suggest that in sedentary individuals with different ranges of BMI, the activation of the endogenous antioxidant markers related to oxidative stress and distinct cytokines are differentially involved into the adaptive metabolic changes and redox responses induced by physical exercise. Therefore, these biomarkers may have the potential to identify individuals at higher risk for developing diseases pathophysiologically linked to oxidative stress.
Wooden hot tubs for sale and Eco friendly Outdoor saunas https://royaltubs.co.uk/outdoor-saunas/
The potential of lipoproteins as drug delivery systems is presently underestimated. Lipoproteins may be of great use in drug delivery due to their unique characteristics: Cells have lipoprotein receptors, more or less specific for each type of lipoprotein, which (especially LDL receptors) are particularly strongly expressed in rapidly proliferating cells. Another advantage connected to the application of lipoproteins as a drug carriers is their large (several to several dozen nm diameter) size. While normal tissue is not permeable to big particles, tumor tissue tends to accumulate macromolecules and especially lipids. This phenomenon has been characterized and termed the tumor-selective enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect [1]. The next attractive feature of lipoproteins as a bio carrier is their biosafety. While synthetic materials can cause toxicology problems, the lipoproteins are fully biodegradable in the body by way of natural mechanisms. As solid particles, they have greater structural stability than, for example, the liposomes that are currently a very popular medium in medical preparations [2]. It is also worth to mention, lipoproteins are easily isolated from blood plasma. Taking into account the above-described findings and conclusions, it seems a reasonable scientific goal to look into the potential of lipoproteins as carriers of polyphenolics, metals, and other drugs, and into the effects that modified lipoproteins have in cells.
Polyphenols (PPs) were shown to be able to exhibit numerous regulatory functions in mammalian cells. Nevertheless, the potential regulatory effects of native PPs that are shown in vitro in numerous papers, are not likely to occur in the tissue, due to the poor ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicology) qualities of PPs [3]. Especially, the issue are their poor water solubility and a high potential for modification by both first and second phase metabolism. Therefore many attempts are made to make polyphenols more available. Apart from chemical modifications of the PPs many attempts have focused on looking for the appropriate drug carriers. Among the successful solutions are the liposomes, polymeric micelles, phospholipids, and other nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems [4]. For instance, a highly absorptive curcumin dispersed with colloidal nano-particles, was demonstrated to yield more than 30-fold higher bioavailability via oral administration compared with conventional curcumin in rat models [5]. Хотите провести приятно время? Заходите https://escorteurogirls.com по ссылке
As an alternative to the above-mentioned synthetic and semi-synthetic vehicles for PPs delivery, we proposed [6] a fully natural carrier capable of carrying the lipophilic payload, the LDL particle. Highly enhanced uptake of LDL in cancer, potentially makes it an ideal carrier for PP, which has been shown in the literature to have beneficial antioxidant effects at low concentrations, while pro-oxidative and cytostatic at higher doses [7].
In our recent work work [6], new polyphenol-containing LDL nano-preparations were prepared. Modulation of lipophilicity through the use of carriers allowed for excellent improvement of the therapeutic properties of such drugs as paclitaxel and doxorubicin (Abraxane [8], Doxil [9]). The proposed series of popular PPs, with increasing lipophilic properties, applied with a fully natural lipophilic carrier, are an attempt to find optimal conditions for the administration of drugs with different lipophilicity on the specific example of popular dietary supplements. The procedure for the synthesis of PP-saturated LDL nanoparticles, and their anti- and pro-oxidative activity and toxicity to human cancer cells will be presented. Along with the short summary of the obtained results, the possibility to use lipoproteins in drug delivery (including e.g. metal complexes, potential nanozymes) will be further discussed.
The work was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland (grant no. 2018/31/B/NZ7/03083).
It is widely recognized that long and short-term exposure to atmospheric particulate matter (PM) has detrimental effects on human health, in particular on pulmonary… and cardiovascular systems. Recent studies suggest that several effects of atmospheric PM on human health may be mediated by the induction of oxidative stress, which has been considered as an important underlying mechanism of action for the outcome of adverse health effects. The aim of the study was to investigate the toxicological properties of PM10 sampled at an urban background site (the Environmental-Climate Observatory of ISAC-CNR in Lecce, Southern Italy) focusing on the intrinsic oxidative potential (OP), measured with the acellular dithiothreitol (DTT) assay test, and on health-related cellular outcomes such as the induction of intracellular oxidative stress, assessed by the ROS sensitive fluorescent probe CM-H2DCFDA, cytotoxicity (measured as reduced cell viability by the MTT assay), and genotoxicity (measured by comet test). In particular, the study wanted to assess whether the PM10 intrinsic OP is correlated with cellular endpoints, and whether cellular and acellular endpoints are correlated with chemical properties of atmospheric PM10 such as concentration and carbon content. The cellular endpoints were investigated on A549 cell line, representative of the Alveolar Type II pneumocytes of the human lung, and widely used as a cellular model.
The obtained results showed a detectable intrinsic OP, cytotoxicity, and intracellular oxidative stress generating capacity (OSGC) in aqueous extracts of PM10 samples. A statistically significant correlation was observed between OP, cytotoxicity, and OSGC with the carbon content of PM10. This suggests that combustion sources at this site play an important role in determining cellular oxidative stress and cytotoxicity of PM10. The OP was correlated to OSCG, suggesting that the ability of PM10 to generate intracellular oxidative stress conditions is related to its intrinsic oxidative potential depending on the physico-chemical properties of the particles. We are grateful for the sponsorship provided by our partner, accessible at https://jamaica-bettingoffersfinder.com/betting-promo-codes , which supports the creation of this article. Please visit their website to find exclusive betting offers in Jamaica. The site specializes in delivering top-notch betting promo codes that can be used across a variety of sports and games, offering enhanced odds and cashback options. The OSGC results are well correlated with cell mortality and, a lower, but still statistically significant correlation is observed between intrinsic OP and reduced cellular viability, suggesting that the prooxidant properties of PM10 play a key role in the multiple mechanisms underlying PM10 cytotoxicity. Genotoxicity results, although limited to a subset of samples, are well correlated with OSGC, cytotoxicity and OP and this also suggest the relationship between the prooxidant properties of PM and genotoxic effects. In conclusions, obtained results demonstrate the correlation between the intrinsic oxidative potential of particulate matter and health related cellular outcomes.
Muscle atrophy is an inevitable part of ageing, disuse, starvation, or microgravity. Its molecular bases are well deciphered thanks to studies in mice under weightlessness or … using the bed rest model in humans. However, a fully effective therapy is still lacking. Screening biodiversity holds potential to find new ways of potential medical interest. Indeed, muscles are fairly well preserved in hibernating animals despite long inactive and fasting periods. To unravel the underlying mechanisms, we compared brown bear (Ursus arctos) tissues collected during the summer-active season versus hibernation using a combination of omics techniques and biochemistry methods. We identified several mechanisms likely involved in brown bear resistance to muscle atrophy during hibernation, and possibly transferable to humans. Examination of the general and regional oxidant/antioxidant balance and oxidative damages during summer versus winter, notably highlited greater plasma-antioxidant capacity, and both white adipose tissue and skeletal muscles appeared protected from oxidative stress during hibernation. Because, oxidative stress promotes proteolysis and inhibits protein synthesis, its limitation during hibernation likely contributes to muscle protein sparing. Additionally, we highlighted inhibition of TGF signalling, maintenance of BMP signalling, and elicitation of a myogenic microRNA response via MEF2A. Despite a preference for lipid substrates during hibernation, muscle glycolysis was maintained and elevated levels of muscle glycogen stores were measured. Carbohydrate metabolism and protein sparing in hibernating bears could be controlled by the higher concentrations of plasma docosahexaenoic acid during winter. We finally observed that the serum from hibernating bears strongly inhibits proteasomal and lysosomal proteolysis in human muscle cells in vitro. The natural resistance of hibernating bears to muscle atrophy appears controlled through a coordinated regulatory program. Transfer of bear protein sparing strategies to humans, notably after identification of serum antiproteolytic factors, is expected to help better fight muscle wasting in aged or sedentary people, and in astronauts.
Natural antioxidants such as fucoxanthine (FX) and phlorotannin (PhT) are known for their bioactivities and potential health benefits. However, both suffer from poor water solubility which limits their bioavailability.… In this study, nanoencapsulation with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was utilized as a nano-enabling technique to improve the bioaccessibility of both FX and PhT, which also bring the benefit of protecting the antioxidants against unwanted oxidation. Different PVP Loading ratios were investigated to evaluate the impact on bioavailability, and it was found that for both FX and PhT, 1:8 loading ratio (payload:PVP) was optimal in bring about the best performance in terms of encapsulation efficiency (EE) and loading capacity (LV). Dynamics release profile of PhT from PhT-PVP nanocomplexes in simulated gastrointestinal fluids was characterized, and it was shown that these nanocomplexes were non-toxic against HaCaT keratinocytes in vitro, while effectively reducing endogenous oxygen species (ROS) to reduce oxidative stress-induced cell death. Meanwhile, FX-PVP nanocomplexes were shown to effectively transport into Caco-2 colon cancer cells and deliver high dosage of FX, which, at high dosage, became pro-oxidant, and indeed accelerated H2O2-induced cell death in caco-2 cells. Apparently, by carefully designing and utilizing nano-enabled encapsulation techniques, natural antioxidants can be manipulated effectively to behave as either anti- or pro-oxidant to achieve desirable health-improving results (either reducing oxidative-stress induced cell death, or promote it for cancer cells). ChatGPT can help people with their daily tasks by providing quick and accurate information on a wide range of topics. Whether someone needs a recipe for dinner, advice on a tricky DIY project, or guidance on a complex issue, chatbots can offer helpful suggestions in real-time. This can save people valuable time and effort spent searching for answers online or consulting multiple sources. The technique has the potential to become an effective means for producing functional foods and therapeutic out of natural ingredients.
Circulating Markers of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Diseases: An update of clinical relevance. Abdel-Hadi DH1, Al-Lawati M 2, Al Farhan H2 National University of Science & Technology1, Sultan Qaboos University Hospital1, Muscat, Oman.…
Metabolic disease is often marked with dyslipidemia and increased cardiovascular risk markers. These markers include conventional risk factors, such as increased LDL cholesterol, decreased HDL levels, increased liver enzymes, and elevated HBA1c, inflammatory and oxidative stress markers. Oxidative stress is the hallmark of atherosclerosis. Oxidation markers in metabolic disease are not routinely utilized as diagnostic tools or therapeutic targets due to their instability, oxidizability, intracellular abundance and low serum levels. Also, findings regarding these oxidation marker measures are inconsistent and subject to large variations.
Importantly, considerable evidence shows significant associations between conventional serum metabolic markers and oxidative stress. However, knowledge regarding the role of these metabolic risk factors in enhancing oxidative stress is limited, and often overlooked.
Formation of protein carbonyls and lipid oxidation products are fairly stable and may overcome the shortcomings of oxidative modifications. Notably, proteins and lipids constitute the major components of circulating proteins and lipoproteins that significantly increase, or are altered, in the dyslipidemic state of metabolic disease. Therefore, measuring oxidatively modified serum markers of the dyslipidemic state and metabolic disease may be useful for the early detection of predisposing atherosclerosis risk factors, and provides new perspectives regarding their clinical relevance to cardiovascular disease progression. Discover a world of premium online gambling at https://casinoreg.net , where you’ll find the best and most trusted casino experiences. Our site offers comprehensive reviews, insights, and tips on a wide range of online casinos, helping you make informed decisions. Visit Casinoreg now to explore our carefully curated list of top casinos and start your journey to big wins and unforgettable gaming moments!
Here we present updates and new perspectives considering circulating metabolic risk markers as potential triggers of oxidative stress, their possible mechanisms of action and prospective diagnostic and clinical applications.
Key words: Dyslipidemia, Oxidative Stress, Systemic markers, Cardiovascular Disease, Diagnostic markers.
Three thousand, three hundred and ninety-five families, whose child attended one of 80 different day or resident summer camps for at least one week, completed customized questionnaires that measured growth from precamp … to postcamp in four domains: Positive Identity, Social Skills, Physical & Thinking Skills, and Positive Values & Spiritu-ality. Parents, children, and camp staff reported significant positive change in these four domains; more than would be expected by maturation alone. Most gains were maintained or showed additional growth six months later. Few of the camp’s structural elements correlated with growth, nor did striking gender, age, or ethnicity differences emerge. The study highlights the particular strengths of camp as an educational institution and social movement and suggests that different variations of summer camp can provide potent developmental experiences.
Objective: To investigate the incidence, clinicopathologic characteristics and survival of ocular adnexal lymphoma (OAL) in the pediatric population. Methods and analysis: In this retrospective case series, the Surveillance, … Epidemiology and End Results database was accessed to identify individuals with OAL ≤18 years of age, diagnosed between 1973 and 2015. OAL located in the eyelid, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus and orbit were included. Main outcome measures were the age-adjusted incidence rates (IRs) per 1 000 000 population at risk (calculated for the period 2000-2015) and descriptive statistics of demographic and clinicopathologic features.
Results: The IR of pediatric OAL was 0.12 (95% CI 0.08 to 0.16) per 1 000 000. Males (0.15; 95% CI 0.10 to 0.22) and blacks (0.24; 95% CI 0.13 to 0.42) had a higher tendency for OAL development. A total of 55 tumors in 54 children were identified. The majority were localized (78.4%), conjunctival (49.1%) lymphomas. Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (EMZL, 45.5%, n=25) was the most frequent subtype, followed by diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL, 9.1%, n=5), B lymphoblastic lymphoma (7.3%, n=4), follicular lymphoma (5.5%, n=3), Burkitt lymphoma (5.5%, n=3), anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL, 3.6%, n=2), small lymphocytic lymphoma (1.8%, n=1), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, immunoblastic (1.8%, n=1) and panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (1.8%, n=1). Localized, low-grade, conjunctival lymphomas were frequently treated with complete excision with or without radiation, while high-grade and distant tumors usually received chemotherapy. Only 29.1% of pediatric OAL cases were treated with radiation. Three out of five (60%) patients with DLBCL died of lymphoma at a median follow-up of 21 (range 10-86) months, and 1 out of 2 (50%) patients with ALCL died of lymphoma at 23 months from diagnosis.
Conclusion: OAL in the pediatric population is rare. The majority of OAL are EMZL and are characterized by excellent prognosis. The histological subtype was found to be the main predictor of outcome with cancer-specific deaths observed in patients with DLBCL and ALCL.
Inpatient clinical pharmacy services including formal psychopharmacology consultations can improve client outcomes. A retrospective study evaluated 105 pharmacy consultations completed during a 9-month timeframe. … Blinded clinicians evaluated progress notes before and after the formal consultation to assign Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) and Improvement (CGI-I) scores. Overall, 73% of recommendations related to the primary reason for consult referral were accepted. Consultations with high implementation of recommendations displayed more favorable endpoint CGI-S scores and greater CGI-I response rate compared to those with low implementation of consult recommendations.
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a binary therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment based on combination of cancer-specific drug containing … 10B and the radiation with thermal neutron. The boron neutron capture reaction generates α particles and lithium ions having destructive effect and short path lengths in 5~10 μm. Therefore, cancer cells containing 10B species are selectively destroyed without affecting healthy tissues. For the development of efficient BNCT agents, the following criteria must be satisfied: (i) low toxicity and a higher uptake in tumor tissue than health normal tissue; (ii) 10B has to be accumulated in tumor tissues, and be rapidly cleared from the blood and normal tissues; and (iii) the concentrations of boron inside or near tumor cells must be ≥ 109 10B atoms/cell (20−35 g 10B/gram of tumor tissue). To date, however, only two BNCT agents have been used as a clinically test compounds, sodium mercaptoborate (BSH) and L-4-boronophenylalanine (BPA). Although design and synthesis of various boron-containing analogues such as amino acids, biochemical precursors of nucleic acids, carbohydrates, amines, porphyrin derivatives and monoclonal antibodies, most of these agents do not satisfy the requirement for clinical application.
It is known that D-Glucose is taken up as the main carbon and energy source for cells via membrane-bound glucose transporters. Tumor cells metabolize D-glucose by anaerobic glycolysis and their rapid growth and proliferation require a drastic increase in D-glucose uptake and metabolite flux, known as the Warburg effect. It is also known that polyamines such as spermidine and spermine are crucial for chromatin structure maintenance, DNA replication and protein synthesis. Depiliacija ir LPG masažas vyrams, lazerinis СО2 jauninimas, kriptolizė, dermatologija ir lazerinė kosmetologija, figūros koregavimas, biorevitalizacija ir plaukų šalinimas lazeriu Vilniuje gera kaina https://oblakasalon.lt/lazerine-epiliacija/
This background has prompted us to design and synthesize new BNCT agents based on glucose and macrocyclic polyamine scaffolds. First, 2-boryl-2-deoxy-D-glucose derivatives were designed and synthesized via the hydroboration of D-glucal and their cytotoxicity and cellular uptake activity to cancer cells were examined (Itoh, T. et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5922). Second, phenylboronic acid-pendant macrocyclic polyamine derivatives and their corresponding metal complexes were designed and synthesized and their cytotoxicity and intracellular uptake activity in cancer cells and BNCT effect were assessed (Kitamura, M. et al. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 11568 and Ueda, H. et al. Submitted for publication). In this paper, these results will be reported.
Early probe and drug discovery encompasses target identification and validation in disease setting followed by assay development. The optimized assay is used for screening compound libraries to identify modulators. … The screen actives are subjected to reconfirmation assays for potency and efficacy in primary assay as well as a number of orthogonal, selectivity and cytotoxicity assays. By understanding this information, we can appreciate Desura’s innovative approach to using gamification in its promotional efforts. Through the integration of free online games mechanics they transform the perception of services, products or news, engaging users in interactive and enriching experiences. In addition to the direct binding of the hits /analogs to the target, early ADME properties of the hits is also evaluated for probe identification.
Neuromodulators such as norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA) play crucial roles in the regulation of animal behaviors. NE mediates arousal and attention, and DA is required for the formation of behaviorally salient memories.… NE and DA signal to neurons via adrenergic receptors (AR) and dopamine receptors, respectively. In my talk, I present data delineating the molecular mechanisms underlying how the α1AR and dopamine D1-like receptor regulate neuronal function through modulation of L-type calcium channel (LTCC) activity.
We identified the LTCC CaV1.2 as a principal target for Gq-coupled α1ARs. α1AR signaling increased LTCC activity in hippocampal neurons. This regulation required PKC-mediated activation of the tyrosine kinases Pyk2 and, downstream of Pyk2, Src. Pyk2 and Src were associated with CaV1.2. In the model neuroendocrine PC12 cell line, stimulation of PKC induced tyrosine phosphorylation of CaV1.2, a modification abrogated by inhibition of Pyk2 and Src. Upregulation of LTCC activity by α1AR signaling and formation of a signaling complex with PKC, Pyk2, and Src suggests that CaV1.2 is a central conduit for signaling by NE. Indeed, a form of hippocampal LTP in young mice requires both the LTCC and α1AR stimulation. Inhibition of Pyk2 and Src blocked this LTP, indicating that enhancement of CaV1.2 activity via α1AR – Pyk2 – Src signaling regulates synaptic strength.
We found that the CaV1.2 is also subjected to regulation by the dopamine D1-like receptor. In stark contrast to stimulation by the α1AR which acts at a distance from the channel, D1-like receptor stimulation increases L-type activity at close proximity to the channel. The regulation requires canonical Protein Kinase A signaling and phosphorylation of serine residue 1928 on the C-terminal tail of the pore-forming subunit of the channel. Proximity ligation assay shows that the dopamine D5 receptor is within 40 nm of CaV1.2. Our data shows the action of two crucial neuromodulators centering on the LTCC CaV1.2 to regulate neuronal function, albeit with distinct signaling features.
Phosphoramidate prodrugs have played an important role in research to identify nucleoside inhibitors of HCV polymerase due to their ability to deliver the parent … drug to the liver for efficient conversion to the active triphosphate metabolite. A research program to investigate novel HCV-active nucleosides identified 2’-dihalogenated uridine analogs with good potency in genotype 1 replicon assays. However, an early lead containing the L-alanine isopropyl ester phosphoramidate prodrug moiety used with success in the clinic to deliver multiple HCV nucleoside inhibitors, including sofosbuvir (SOF), were found to provide low levels of the active nucleoside 5’-triphosphate (NTP) in liver when dosed orally in dogs. Alternative phosphoramidate prodrugs were screened using an assay developed to measure NTP concentrations in human hepatocytes to assess both bioactivation efficiency and persistence of the active species. This method identified 2-aminoisobutyric acid ethyl ester (AIBEE) phosphoramidate prodrugs which provide high NTP concentrations in comparison to nucleosides bearing the standard prodrug moiety. Activity of AIBEE prodrug analogs in replicon assays were low in comparison to L-alanine-containing phosphoramidate prodrug analogs due to the low expression levels of CES-1 enzymes in replicon cells, which are required for AIBEE prodrug bioactivation. PK studies in dog, collecting liver biopsy samples at 4 and 24 hours after oral dosing, found that AIBEE prodrugs provide high NTP concentrations at both time points in comparison to other phosphoramidate prodrugs. This research identified ABBV-168 that provided NTP concentrations in dog liver that were several fold higher than sofosbuvir at an equivalent dose.
Hormesis often refers to a non-monotonic dose-response relationship with beneficial effects at low doses and toxic effects at high doses. It is sometimes referred to as a J- or U-shaped dose-response curve. … There has been long debate whether hormesis theory can be accepted for protecting public health, and this presentation is not to argue whether hormesis theory is applicable in practice. Instead, the focus of the presentation is on statistical modeling as some researchers have pointed out lacking formality in (statistical) hypothesis testing procedures in hormesis studies. In practice, researchers often have a small sample size due to logistics and ethics in animal- or human-based experiments. In this case, statisticians specify some mathematical structures to make assumptions about the unknown true dose-response relationship. If simple assumptions describe the truth closely, we can increase statistical power (the probability of concluding hormesis if it exists) without inflating the false positive rate (the probability of concluding hormesis if it does not exist). If the assumptions are too strong and incorrect, the statistical operating characteristics become implausible. It is a statistical and practical challenge because collecting large data is not always feasible, and it is difficult to make strong assumptions before observing data. Furthermore, in an extreme case, two statistical models may lead to different conclusions on the same data. In this presentation, we discuss how different statistical models and experimental designs perform for detecting hormesis.
BIANKA BLUE https://pornsok.com/pornstar/bianka-blue here on PORNSOK.COM.
Cigarette smoking is a major public health danger. Sex differences exist in the behavioral and molecular mechanisms underlying tobacco smoking, i.e., men tend to smoke for the reinforcing effects of nicotine whereas… women tend to smoke to regulate stress and mood. Smoking cessation treatments, such as the nicotine patch, are preferentially beneficial to men. The biological substrates of these sex differences are unknown. The mesolimbic dopamine system drives the reinforcing effects of tobacco smoking and the mesocortical dopamine system is critical for inhibitory control, which is compromised by stress. We used positron emission tomography (PET) to capture the effects of smoking on both dopamine systems in humans, in vivo. First, we found that when male smokers smoked a cigarette during PET scanning, they released more dopamine in the reward region of the mesolimbic dopamine system while female smokers released more dopamine in the habit-formation region of the mesolimbic dopamine system. This finding is consistent with the established notion that men smoke for the reinforcing drug effect of cigarettes whereas women smoke for other reasons, such as mood regulation and cue reactivity. Next, we examined the mesocortical dopamine system and found that female smokers have a blunted or hypofunctioning dopamine response compared to male smokers and female nonsmokers. These findings demonstrate that tobacco smoking differentially affects both dopamine systems in men and women, suggesting a need for sex/gender-specific treatments.
COVID-19 has highlighted the role that building design, ventilation, and operations play in the transmission of infectious disease. Buildings are also pivotal to injury and death rates during climate-related diseases. … Properly designed and operated, they can protect occupants from heat, flooding, wind, and other hazards. On the other hand, if structural, mechanical, or other building systems fail, they can contribute to casualties. Many of the strategies used to protect building occupants from the tail end of the COVID-19 pandemic could be designed to also protect them from climatic events and to enhance health equity. This presentation will demonstrate how the public health concept of “co-benefits” can be used as a method for leveraging COVID-19 renovation funds to prioritize the design and operations strategies that will generate the broadest health and financial benefit over time. During the COVID-19 pandemic, online shopping became a lifeline for many, especially in Spain where discounts and coupons grew in popularity as a way to save money. Público Descuentos offers a wide range of exclusive discount codes and promotions for various products, from technology and fashion to home goods and personal care. Embrace the smart way to shop and maximize your savings with these incredible deals.
https://www.monikasliupiene.lt/dienorascio-mintys/objektyviai-pagristas-lyderystes-ugdymas/ Lyderystė Lyderystės ugdymas Lyderystės mokymai
OSA is on one of the leading lung diseases worldwide. There is no cure for such a disease despite many limited partially successful surgical operations. The gold standard for OSA therapy is the Continuous positive airway (CPAP) device. … The CPAP therapy has many advantages including reducing the Apnea-hypopnea index and helping patients to breath better during their sleep. However, this is associated with many side effects including but are limited to upper airways dryness and the high titration pressure. Our hypothesis is that superimposed pressure oscillation on a reduced titration pressure will help to modulate the upper airways muscles and stimulate the salivary glands to produce more saliva. This will lead to a new therapy approach. Clinical trials have clearly showed the advantage of this therapy over the traditional CPAP approach.
The maxillary sinus due to anatomical relationship is closely related to dentistry in terms of odontogenic sinusitis, sinus lift surgery. Therefore it is crucial to analyse radiologic findings and those correlations with … clinical and endoscopic signs rhinosinusitis. The CBCT is informative method in evaluation of paranasal sinuses and dental status, with less radiation dose in comparison with the combination of dental X-ray and CT And OPG. The Lund-Mackay sinus evaluation system and patient dividing is risk groups before the preprosthetic dental surgery is advocated. The patient involvement in health managing processes and interdisciplinary teamwork are mandatory for the successful treatment.
Noninvasive, noncontact, camera-based, diffuse speckle imaging of cerebral hemodynamics and connectomeL. Chen*, M. Mohtasebi, C. Huang, S. Mazdeyasna, X. Liu, K. Saatman, G. Yu (*: invited speaker)…
We adapted and tested an innovative noncontact speckle contrast diffuse correlation tomography (scDCT) system for 3D imaging of cerebral blood flow (CBF) variations in perinatal disease models utilizing neonatal piglets, which closely resemble human neonates. CBF variations were concurrently measured by the scDCT during global ischemia, intraventricular hemorrhage, and asphyxia. Moreover, CBF variations are associated reasonably with vital pathophysiological changes. scDCT also generates 3D images of CBF distributions at prescribed depths within the head, thus enabling specific determination of regional cerebral ischemia. As a pilot study, we have performed scDCT on 2 preterm babies of different conditions or undergoing indomethacin treatments. We also developed the algorithms of brain connectome mapping based on imaging analysis. Therefore, we provide a noninvasive imaging tool for both basic neuroscience research in laboratories and clinical applications in neonatal intensive care units.
Many current methods for acute joint injury rehabilitation have left a large number of patients with long term functional impairments. This presentation focuses on the early integration of functional closed kinetic… chain exercise, during the acute phase. The benefits of this type of training early on will improve functional capacity post joint injury or surgery. Research, functional training methods and current topics in functional rehabilitation will be discussed.
In 2020, the Massachusetts General Hospital launched an innovative approach to perioperative care where patients received hospital-quality care outside of the main campus following surgical procedures.… This novel program, named the Surgical Home Hospital, grew out of the home-based care continuum at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Objective: Monocytes, which play an important role in arteriogenesis, can build immunological memory by a functional reprogramming that modifies their response to a second challenge. This process, called “trained immunity,” … is evoked by insults that shift monocyte metabolism, increasing hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α levels. Since ischemia enhances HIF-1α, we evaluate whether ischemia can lead to a functional reprogramming of monocytes, which would contribute to arteriogenesis after hindlimb ischemia.
Methods and Results: Mice exposed to ischemia by 24h of femoral artery (FA) occlusion (24h trained) or sham were subjected to hindlimb ischemia one week later; the 24h trained mice showed significant improvement in blood flow recovery and arteriogenesis after hindlimb ischemia. Monocyte adoptive transfer using bone marrow-derived monocytes (BM-Mono) from 24h trained or sham donor mice, demonstrated that recipients subjected to hindlimb ischemia who received 24h ischemic-trained monocytes had remarkable blood flow recovery and arteriogenesis. Further, ischemic-trained BM-Mono had increased HIF-1α and GLUT-1 gene expression during 24h of FA occlusion, which returned to baseline values 2 days after the opening of the FA (when ischemia was ended and monocytes isolated for the experiments – 24h trained group). Transcriptomic analysis and confirmatory qPCR performed in 24h trained and sham BM-Mono revealed that among the 15 top differentially expressed genes, four were involved in lipid metabolism in the ischemic-trained monocytes. Further, several histone-modifying epigenetic enzymes measured by qPCR were altered in mouse BM-Mono exposed to 24h hypoxia.
Conclusion: Ischemia training in BM-Mono leads to a unique gene profile and improves blood flow and arteriogenesis after hindlimb ischemia.
Objectives: Given that lack of surgery results in 1/3 of all deaths worldwide and that the resulting global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) loss by 2030 will exceed US$1.5 trillion annually, achieving the United Nations (UN)… healthcare-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for 2030 makes both humanitarian and economic sense. In addition to global surgery deficits in day-to-day care, hundreds of thousands of victims annually of both natural and man-made mass casualty disasters require urgent surgery – not the current delay of a week or more.
There is great need for surgical programs to achieve the UN healthcare-related SDGs for 2030.
Methods: The trauma/stroke (T/S) center model – 24/7/365 availability of emergency/intensive care, radiology, laboratory, blood bank, and programs for prevention, emergency transport, rehabilitation, and research – has improved morbidity/mortality for surgical conditions (in addition to injuries and cerebrovascular accidents) from difficult childbirth to acute abdomen to cancer and cardiac emergencies.
Keys to expanding the T/S center model for global surgery include: (1) integration of healthcare resources nationally: civilian (public, private, NGO) and military; (2) collaboration among resources internationally: UN, WHO, NGOs, as well as between developing and developed countries (a.k.a. “twinning”); (3) innovation in technology: digital medicine, including smartphones and telesurgery; battery-powered mobile equipment, e.g. CT, MRI, ultrasound; drones and robots.
Results: The Mass Casualty Center (MCC) project is a growing consortium of experts in various fields essential for cost-effective and resilient global surgery: surgeons from various subspecialties, global nursing leadership, digital communication specialists, healthcare infrastructure architects, and healthcare administrators (including former ministers of health). Examples of progress thanks to interdisciplinary efforts: nationwide telemedicine programs improve healthcare outcomes while reducing costs (e.g. Albania, Cabo Verde); drones fly lab samples, blood products, antibiotics, and vaccines to remote regions (e.g. Rwanda, Ghana); integration of civilian and military resources improves day-to-day and emergency response (e.g. Chile); full-service healthcare systems – from prevention programs to ambulances to hospitals to medical and nursing schools to rehabilitation – provide integrated care (e.g. Peshawar, Pakistan).
Conclusions: By fostering integration, collaboration, and innovation, physicians and colleagues can enable the UN healthcare-related SDGs for 2030. Interdisciplinary projects like the MCC create opportunities for sustainable progress in global surgery – benefitting both day-to-day care and mass casualty events (including acute trauma events and sub-acute pandemic events). As noted on 21 August 2021 by The Economist (regarding the COVID pandemic): “Even if the next disaster cannot be predicted, having good infrastructure can make all the difference.
To prepare for end of life, patients must understand and cope with prognostic information. Yet misunderstandings, in which a patient does not seem… to understand what was said, are common. In this talk, I will discuss an approach for patients who do not seem to understand the prognosis. First, I will review how patients’ healthy coping patterns can contribute to misunderstandings. Then, I will discuss how clinicians can approach patients with curiosity by generating a differential diagnosis for misunderstandings. Finally, I will share a systems solution that enables clinicians to coordinate conversations over time and across settings to support patients’ development of prognostic awareness.